Heat shock protein 47 and 65-kDa FK506-binding protein weakly but synergistically interact during collagen folding in the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 28860186
- PMCID: PMC5655501
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.802298
Heat shock protein 47 and 65-kDa FK506-binding protein weakly but synergistically interact during collagen folding in the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
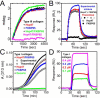
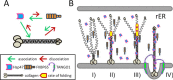
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the extracellular matrix in humans and is critical to the integrity and function of many musculoskeletal tissues. A molecular ensemble comprising more than 20 molecules is involved in collagen biosynthesis in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Two proteins, heat shock protein 47 (Hsp47/SERPINH1) and 65-kDa FK506-binding protein (FKBP65/FKBP10), have been shown to play important roles in this ensemble. In humans, autosomal recessive mutations in both genes cause similar osteogenesis imperfecta phenotypes. Whereas it has been proposed that Hsp47 and FKBP65 interact in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, there is neither clear evidence for this interaction nor any data regarding their binding affinities for each other. In this study using purified endogenous proteins, we examined the interaction between Hsp47, FKBP65, and collagen and also determined their binding affinities and functions in vitro Hsp47 and FKBP65 show a direct but weak interaction, and FKBP65 prefers to interact with Hsp47 rather than type I collagen. Our results suggest that a weak interaction between Hsp47 and FKBP65 confers mutual molecular stability and also allows for a synergistic effect during collagen folding. We also propose that Hsp47 likely acts as a hub molecule during collagen folding and secretion by directing other molecules to reach their target sites on collagens. Our findings may explain why osteogenesis imperfecta-causing mutations in both genes result in similar phenotypes.
Keywords: collagen; endoplasmic reticulum (ER); molecular chaperone; protein folding; protein-protein interaction.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction between KDELR2 and HSP47 as a Key Determinant in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Bi-allelic Variants in KDELR2.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov 5;107(5):989-999. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 33053334 Free PMC article.
-
HSP47 and FKBP65 cooperate in the synthesis of type I procollagen.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Apr 1;24(7):1918-28. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu608. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25510505 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygosity for a missense mutation in SERPINH1, which encodes the collagen chaperone protein HSP47, results in severe recessive osteogenesis imperfecta.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Mar 12;86(3):389-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.01.034. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20188343 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the endoplasmic reticulum-resident, collagen-specific molecular chaperone Hsp47 in vertebrate cells and human disease.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 8;294(6):2133-2141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.002812. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30541925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteogenesis imperfecta due to mutations in non-collagenous genes: lessons in the biology of bone formation.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014 Aug;26(4):500-7. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000117. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 25007323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of Hyaluronan synthase 2 suppresses liver fibrosis in mice via induction of transcriptomic changes similar to 4MU treatment.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 2;14(1):2797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53089-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38307876 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between KDELR2 and HSP47 as a Key Determinant in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Caused by Bi-allelic Variants in KDELR2.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Nov 5;107(5):989-999. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 33053334 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin B control of lysine post-translational modifications of skin type I collagen.PLoS Genet. 2019 Jun 7;15(6):e1008196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008196. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31173582 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP10 promotes proliferation of glioma cells via activating AKT-CREB-PCNA axis.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Feb 9;28(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00705-3. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 33557829 Free PMC article.
-
FK506-Binding Protein 13 Expression Is Upregulated in Interstitial Lung Disease and Correlated with Clinical Severity. A Potentially Protective Role.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Feb;64(2):235-246. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0121OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33253593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bächinger H. P., Mizuno K., Vranka J., and Boudko S. (2010) Collagen Formation and Structure. In Comprehensive Natural Products II: Chemistry and Biology (Mander L., and Liu H.-W. eds.) pp. 469–530, Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc., New York
-
- Bateman J. F., Boot-Handford R. P., and Lamandé S. R. (2009) Genetic diseases of connective tissues: cellular and extracellular effects of ECM mutations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 173–183 - PubMed
-
- Bella J., and Hulmes D. J. (2017) Fibrillar Collagens. Subcell. Biochem. 82, 457–490 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

