Whole blood clot optical clearing for nondestructive 3D imaging and quantitative analysis
- PMID: 28856043
- PMCID: PMC5560833
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.8.003671
Whole blood clot optical clearing for nondestructive 3D imaging and quantitative analysis
Abstract
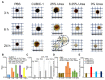
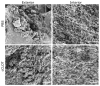
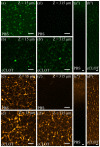
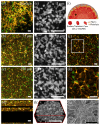
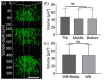
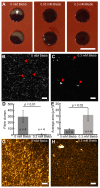
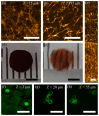
A technological revolution in both light and electron microscopy imaging now allows unprecedented views of clotting, especially in animal models of hemostasis and thrombosis. However, our understanding of three-dimensional high-resolution clot structure remains incomplete since most of our recent knowledge has come from studies of relatively small clots or thrombi, due to the optical impenetrability of clots beyond a few cell layers in depth. Here, we developed an optimized optical clearing method termed cCLOT that renders large whole blood clots transparent and allows confocal imaging as deep as one millimeter inside the clot. We have tested this method by investigating the 3D structure of clots made from reconstituted pre-labeled blood components yielding new information about the effects of clot contraction on erythrocytes. Although it has been shown recently that erythrocytes are compressed to form polyhedrocytes during clot contraction, observations of this phenomenon have been impeded by the inability to easily image inside clots. As an efficient and non-destructive method, cCLOT represents a powerful research tool in studying blood clot structure and mechanisms controlling clot morphology. Additionally, cCLOT optical clearing has the potential to facilitate imaging of ex vivo clots and thrombi derived from healthy or pathological conditions.
Keywords: (170.1790) Confocal microscopy; (170.3660) Light propagation in tissues; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.6935) Tissue characterization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathologically stiff erythrocytes impede contraction of blood clots.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Aug;19(8):1990-2001. doi: 10.1111/jth.15407. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34233380 Free PMC article.
-
Blood clot contraction: Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and disease.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022 Dec 23;7(1):100023. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2022.100023. eCollection 2023 Jan. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 36760777 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Contraction of Blood Clots in Venous Thromboembolism Is a Potential Thrombogenic and Embologenic Mechanism.TH Open. 2018 Mar 28;2(1):e104-e115. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1635572. eCollection 2018 Jan. TH Open. 2018. PMID: 31249934 Free PMC article.
-
Considerations for using optical clearing techniques for 3D imaging of nanoparticle biodistribution.Int J Pharm. 2020 Oct 15;588:119739. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119739. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32783979 Review.
-
Light microscopy of whole plant organs.J Microsc. 2016 Aug;263(2):165-70. doi: 10.1111/jmi.12394. Epub 2016 Mar 29. J Microsc. 2016. PMID: 27027806 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Developments in Tissue Optical Clearing Aid Super-Resolution Microscopy Imaging?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 23;22(13):6730. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136730. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombus Structural Composition in Cardiovascular Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 Sep;41(9):2370-2383. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315754. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 34261330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non contrast enhanced volumetric histology of blood clots through high resolution propagation-based X-ray microtomography.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 17;12(1):2778. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-06623-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35177767 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue clearing to examine tumour complexity in three dimensions.Nat Rev Cancer. 2021 Nov;21(11):718-730. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00382-w. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34331034 Review.
-
Modulating the rate of fibrin formation and clot structure attenuates microvascular thrombosis in systemic inflammation.Blood Adv. 2020 Apr 14;4(7):1340-1349. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001500. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32259201 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
