Combined targeting of Arf1 and Ras potentiates anticancer activity for prostate cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 28830537
- PMCID: PMC5568197
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-017-0583-4
Combined targeting of Arf1 and Ras potentiates anticancer activity for prostate cancer therapeutics
Abstract
Background: Although major improvements have been made in surgical management, chemotherapeutic, and radiotherapeutic of prostate cancer, many prostate cancers remain refractory to treatment with standard agents. Therefore, the identification of new molecular targets in cancer progression and development of novel therapeutic strategies to target them are very necessary for achieving better survival for patients with prostate cancer. Activation of small GTPases such as Ras and Arf1 is a critical component of the signaling pathways for most of the receptors shown to be upregulated in advanced prostate cancer.
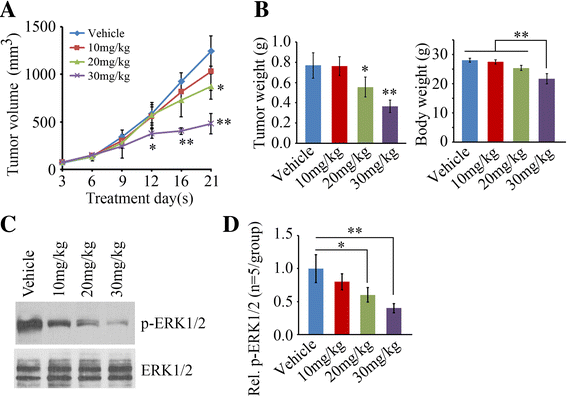
Methods: The drug effects on cell proliferation were measured by CellTiter 96® AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. The drug effects on cell migration and invasion were determined by Radius™ 24-well and Matrigel-coated Boyden chambers. The drug effects on apoptosis were assessed by FITC Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit with 7-AAD and Western blot with antibodies against cleaved PARP and Caspase 3. A NOD/SCID mouse model generated by subcutaneous injection was used to assess the in vivo drug efficacy in tumor growth. ERK activation and tumor cell proliferation in xenografts were examined by immunohistochemistry.
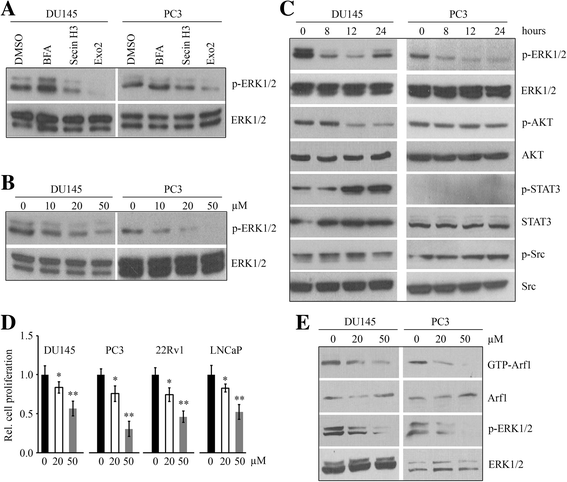
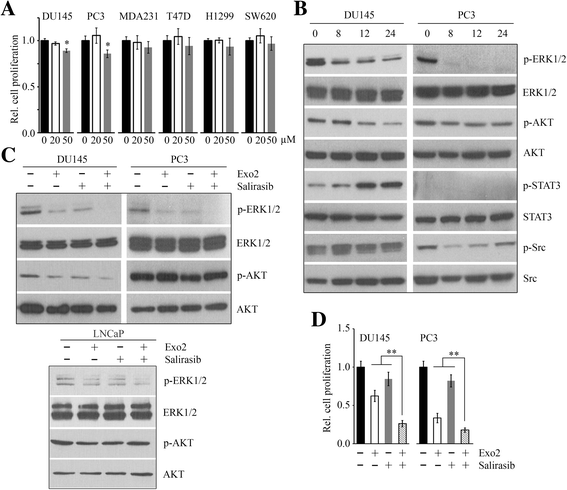
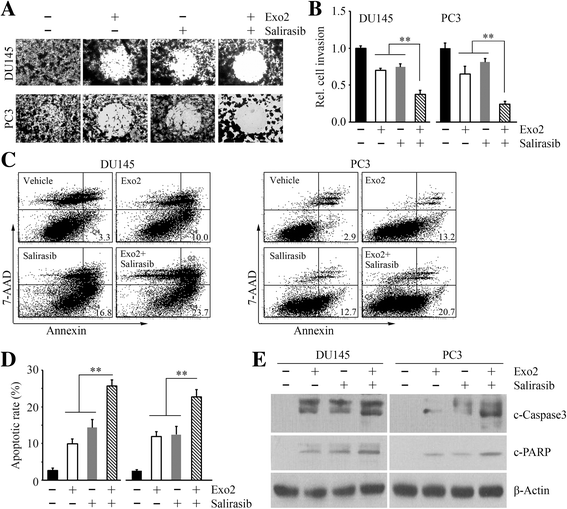
Results: We show that Exo2, a small-molecule inhibitor that reduces Arf1 activation, effectively suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation by blocking ERK1/2 activation. Exo2 also has other effects, inhibiting migration and invasion of PCa cells and inducing apoptosis. The Ras inhibitor salirasib augments Exo2-induced cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells partially by enhancing the suppression of ERK1/2 phosphorylation. In a xenograft mouse model of prostate cancer, Exo2 reduces prostate tumor burden and inhibits ERK1/2 activation at a dose of 20 mg/kg. Synergistic treatment of salirasib and Exo2 exhibits a superior inhibitory effect on prostate tumor growth compared with either drug alone, which may be attributed to the more efficient inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
Conclusion: This study suggests that simultaneous blockade of Arf1 and Ras activation in prostate cancer cells is a potential targeted therapeutic strategy for preventing prostate cancer development.
Keywords: Arf1; Combination treatment; Exo2; Prostate cancer; Ras; Salirasib.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Augusta University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
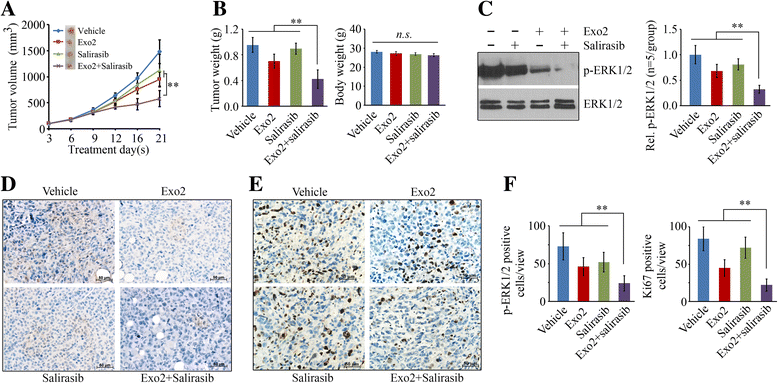
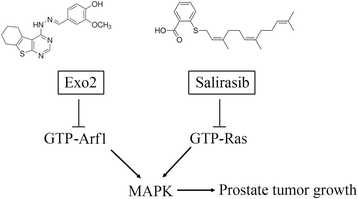
Similar articles
-
Augmentation of the anticancer activity of CYT997 in human prostate cancer by inhibiting Src activity.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jun 12;10(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0485-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28606127 Free PMC article.
-
HRAS as a potential therapeutic target of salirasib RAS inhibitor in bladder cancer.Int J Oncol. 2018 Aug;53(2):725-736. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4435. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29901113
-
Salirasib inhibits the growth of hepatocarcinoma cell lines in vitro and tumor growth in vivo through ras and mTOR inhibition.Mol Cancer. 2010 Sep 22;9:256. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-256. Mol Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20860815 Free PMC article.
-
Salirasib in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.Future Oncol. 2010 Jun;6(6):885-91. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.71. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20528225 Review.
-
Signal transduction by Ras-like GTPases: a potential target for anticancer drugs.Gene Expr. 1995;4(6):345-56. Gene Expr. 1995. PMID: 7549466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional disruption of the Golgi apparatus protein ARF1 sensitizes MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells to the antitumor drugs Actinomycin D and Vinblastine through ERK and AKT signaling.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 3;13(4):e0195401. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195401. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29614107 Free PMC article.
-
GTPase Pathways in Health and Diseases.Cells. 2022 Dec 15;11(24):4055. doi: 10.3390/cells11244055. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552819 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ARF1-IQGAP1 interaction to suppress colorectal cancer metastasis and vemurafenib resistance.J Adv Res. 2023 Sep;51:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2022.11.006. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36396045 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of differentially expressed genes in cadmium-induced prostate carcinogenesis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 15;375:57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 May 11. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31082426 Free PMC article.
-
The involvement of FBP1 in prostate cancer cell epithelial mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway.Cell Cycle. 2019 Oct;18(19):2432-2446. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1648956. Epub 2019 Aug 25. Cell Cycle. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2022 Dec;21(24):2670. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2137762 PMID: 31448674 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

