Transient expression of ZBTB32 in anti-viral CD8+ T cells limits the magnitude of the effector response and the generation of memory
- PMID: 28827827
- PMCID: PMC5578684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006544
Transient expression of ZBTB32 in anti-viral CD8+ T cells limits the magnitude of the effector response and the generation of memory
Abstract
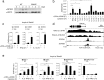
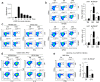
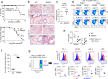
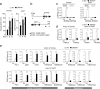
Virus infections induce CD8+ T cell responses comprised of a large population of terminal effector cells and a smaller subset of long-lived memory cells. The transcription factors regulating the relative expansion versus the long-term survival potential of anti-viral CD8+ T cells are not completely understood. We identified ZBTB32 as a transcription factor that is transiently expressed in effector CD8+ T cells. After acute virus infection, CD8+ T cells deficient in ZBTB32 showed enhanced virus-specific CD8+ T cell responses, and generated increased numbers of virus-specific memory cells; in contrast, persistent expression of ZBTB32 suppressed memory cell formation. The dysregulation of CD8+ T cell responses in the absence of ZBTB32 was catastrophic, as Zbtb32-/- mice succumbed to a systemic viral infection and showed evidence of severe lung pathology. We found that ZBTB32 and Blimp-1 were co-expressed following CD8+ T cell activation, bound to each other, and cooperatively regulated Blimp-1 target genes Eomes and Cd27. These findings demonstrate that ZBTB32 is a key transcription factor in CD8+ effector T cells that is required for the balanced regulation of effector versus memory responses to infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signal 3 requirement for memory CD8+ T-cell activation is determined by the infectious pathogen.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Nov;41(11):3176-86. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141537. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21830209
-
Gammaherpesvirus latency differentially impacts the generation of primary versus secondary memory CD8+ T cells during subsequent infection.J Virol. 2014 Nov;88(21):12740-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02106-14. Epub 2014 Aug 20. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 25142586 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Functional Alterations in Circulating Memory CD8 T Cells with Time after Primary Infection.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Oct 20;11(10):e1005219. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005219. eCollection 2015 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26485703 Free PMC article.
-
Making memories that last a lifetime: heritable functions of self-renewing memory CD8 T cells.Int Immunol. 2010 Oct;22(10):797-803. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxq437. Epub 2010 Aug 23. Int Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20732857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surviving the crash: transitioning from effector to memory CD8+ T cell.Semin Immunol. 2009 Apr;21(2):92-8. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Semin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19269192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imbalance of Regulatory and Cytotoxic SARS-CoV-2-Reactive CD4+ T Cells in COVID-19.Cell. 2020 Nov 25;183(5):1340-1353.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Cell. 2020. PMID: 33096020 Free PMC article.
-
Tfh-cell-derived interleukin 21 sustains effector CD8+ T cell responses during chronic viral infection.Immunity. 2022 Mar 8;55(3):475-493.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.01.018. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Immunity. 2022. PMID: 35216666 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Regulatory Circuits in Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells.Annu Rev Immunol. 2022 Apr 26;40:387-411. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-101320-025949. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35119910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inherited KDM6AA649T facilitates tumor-immune escape and exacerbates colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma outcomes.Oncogene. 2024 Jun;43(23):1757-1768. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03029-w. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38622203
-
Clonal expansion of innate and adaptive lymphocytes.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Nov;20(11):694-707. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0307-4. Epub 2020 May 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32424244 Review.
References
-
- Lauvau G, Boutet M, Williams TM, Chin SS, Chorro L. Memory CD8+ T Cells: Innate-Like Sensors and Orchestrators of Protection. Trends Immunol. Elsevier Ltd; 2016;37: 375–385. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.04.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doering TA, Crawford A, Angelosanto JM, Paley MA, Ziegler CG, Wherry EJ. Network Analysis Reveals Centrally Connected Genes and Pathways Involved in CD8(+) T Cell Exhaustion versus Memory. Immunity. 2012;37: 1130–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Best JA, Blair DA, Yang E, Mayya V, Doedens A, Dustin ML, et al. Transcriptional insights into the CD8(+) T cell response to infection and memory T cell formation. Nat Immunol. 2013;14: 404–412. doi: 10.1038/ni.2536 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu G, Chen J. A genome-wide regulatory network identifies key transcription factors for memory CD8. Nature Communications. Nature Publishing Group; 2013;4: 1–14. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3830 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buchholz VR, Flossdorf M, Hensel I, Kretschmer L, Weissbrich B, Gräf P, et al. Disparate individual fates compose robust CD8+ T cell immunity. Science. American Association for the Advancement of Science; 2013;340: 630–635. doi: 10.1126/science.1235454 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI124299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI084987/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI109858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI048785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI046629/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048785/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI066232/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI017672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI074699/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI101976/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI017672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI106833/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI118326/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

