Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in the Dorsomedial Striatum Is a Novel Positive Regulator of Alcohol Consumption
- PMID: 28821667
- PMCID: PMC6596666
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0890-17.2017
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in the Dorsomedial Striatum Is a Novel Positive Regulator of Alcohol Consumption
Abstract
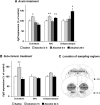
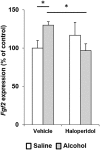
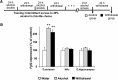
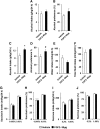
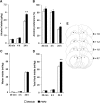
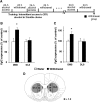
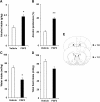
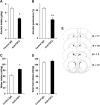
Repeated alcohol intake leads to mesostriatal neuroadaptations, resulting in drinking escalation and addiction phenotypes. Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) has been shown to interact with the mesostriatal dopaminergic system, and has been implicated in the actions of psychostimulants in the brain, and in several psychiatric disorders. Here, we report on a positive regulatory feedback loop of alcohol and FGF2 in rodent models. Specifically, we found that acute alcohol exposure (2.5 g/kg, i.p.) increased the mRNA expression of Fgf2 in the dorsal hippocampus, nucleus accumbens, and dorsal striatum. Longer alcohol exposure (7 d × 2.5 g/kg, i.p.) restricted these increases to the dorsal striatum, and the latter effect was blocked by the dopamine D2-like receptor antagonist haloperidol. Voluntary prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption in a 2-bottle choice procedure increased Fgf2 expression selectively in dorsomedial striatum (DMS) of both mice and rats. Importantly, we found that systemic administration of recombinant FGF2 (rFGF2) in mice, or rFGF2 infusion into the dorsal striatum or DMS of rats, increased alcohol consumption and preference, with no similar effects on saccharin or sucrose consumption. Finally, we found that inhibition of the endogenous FGF2 function in the DMS, by an anti-FGF2 neutralizing antibody, suppressed alcohol consumption and preference. Together, our results suggest that alcohol consumption increases the expression of Fgf2 in the DMS, and that striatal FGF2 promotes alcohol consumption, suggesting that FGF2 in the DMS is a positive regulator of alcohol drinking.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Long-term alcohol intake may lead to neuroadaptations in the mesostriatal reward system, resulting in addiction phenotypes. Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) is crucial for the development and maintenance of the mesostriatal dopaminergic system. Here, we provide evidence for the involvement of FGF2 in alcohol-drinking behaviors. We show that alcohol increases Fgf2 expression in the dorsal striatum, an effect mediated via dopamine D2-like receptors. Importantly, we show that infusion of recombinant FGF2 into the dorsomedial striatum increases alcohol consumption, whereas inhibiting the endogenous FGF2 function suppresses consumption. Thus, FGF2 is an alcohol-responsive gene constituting a positive regulatory feedback loop with alcohol. This loop leads to facilitation of alcohol consumption, marking FGF2 as a potential new therapeutic target for alcohol addiction.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol; dopamine; dorsomedial striatum; fibroblast growth factor 2.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/378742-13$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of FGF Receptor-1 Suppresses Alcohol Consumption: Role of PI3 Kinase Signaling in Dorsomedial Striatum.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 2;39(40):7947-7957. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0805-19.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 2. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31375540 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 is an endogenous regulator of alcohol reward and consumption.Addict Biol. 2022 Mar;27(2):e13115. doi: 10.1111/adb.13115. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 34796591
-
Alcohol Elicits Functional and Structural Plasticity Selectively in Dopamine D1 Receptor-Expressing Neurons of the Dorsomedial Striatum.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 19;35(33):11634-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0003-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26290240 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal involvement in human alcoholism and alcohol consumption, and withdrawal in animal models.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Oct;35(10):1739-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01520.x. Epub 2011 May 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21615425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of fibroblast growth factor 2 in drug addiction.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Aug;50(3):2552-2561. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14133. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30144335 Review.
Cited by
-
New developments in the biology of fibroblast growth factors.WIREs Mech Dis. 2022 Jul;14(4):e1549. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1549. Epub 2022 Feb 9. WIREs Mech Dis. 2022. PMID: 35142107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-type specific changes in PKC-delta neurons of the central amygdala during alcohol withdrawal.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Jul 20;12(1):289. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02063-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35859068 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis to explore the mechanism of downregulated TNIK influencing the effect of risperidone.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 23;15:1431923. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1431923. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39268461 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of FGF Receptor-1 Suppresses Alcohol Consumption: Role of PI3 Kinase Signaling in Dorsomedial Striatum.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 2;39(40):7947-7957. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0805-19.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 2. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31375540 Free PMC article.
-
The neurokinin-1 receptor mediates escalated alcohol intake induced by multiple drinking models.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Jul 15;137:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 3. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29758386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) The diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Ed 5 Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

