Metformin Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Tumor Growth of Breast Cancer Cells by Upregulating miR-200c but Downregulating AKT2 Expression
- PMID: 28819383
- PMCID: PMC5556649
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.19858
Metformin Inhibits Tumorigenesis and Tumor Growth of Breast Cancer Cells by Upregulating miR-200c but Downregulating AKT2 Expression
Abstract
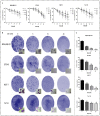
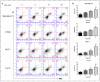
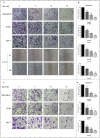
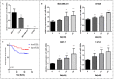
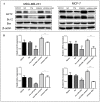
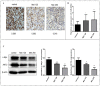
Background: Metformin has been reported to inhibit the growth of various types of cancers, including breast cancer. Yet the mechanisms underlying the anticancer effects of metformin are not fully understood. Growing evidence suggests that metformin's anticancer effects are mediated at least in part by modulating microRNAs, including miR-200c, which has a tumor suppressive role in breast cancer. We hypothesized that miR-200c has a role in the antitumorigenic effects of metformin on breast cancer cells. Methods: To delineate the role of miR-200c in the effects of metformin on breast cancer, plasmids containing pre-miR-200c or miR-200c inhibitor were transfected into breast cancer cell lines. The MDA-MB-231, BT549, MCF-7, and T-47-D cells' proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were assessed. The antitumor role of metformin in vivo was investigated in a MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor model in SCID mice. Results: Metformin significantly inhibited the growth, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells, and induced their apoptosis; these effects were dependent on both dose and time. Metformin also suppressed MDA-MB-231 tumor growth in SCID mice in vivo. Metformin treatment was associated with increased miR-200c expression and decreased c-Myc and AKT2 protein expression in both breast cancer cells and tumor tissues. Overexpression of miR-200c exhibited effects on breast cancer cells similar to those of metformin treatment. In contrast, inhibiting the expression of miR-200c increased the growth, migration, and invasion of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Conclusion: Metformin inhibits the growth and invasiveness of breast cancer cells by upregulation of miR-200c expression by targeting AKT2. These findings provide novel insight into the molecular functions of metformin that suggest its potential as an anticancer agent.
Keywords: AKT2; Metformin; breast cancer cell; miR-200c.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
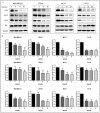
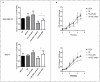
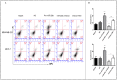
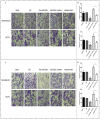

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of the miR-141/200c cluster promotes the migratory and invasive ability of triple-negative breast cancer cells through the activation of the FAK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways by secreting VEGF-A.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 2;16:570. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2620-7. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27484639 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200c/PAI-2 promotes the progression of triple negative breast cancer via M1/M2 polarization induction of macrophage.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Apr;81:106028. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106028. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31801690
-
Knockdown of circDENND4C inhibits glycolysis, migration and invasion by up-regulating miR-200b/c in breast cancer under hypoxia.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 5;38(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1398-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31488193 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin may function as anti-cancer agent via targeting cancer stem cells: the potential biological significance of tumor-associated miRNAs in breast and pancreatic cancers.Ann Transl Med. 2014 Jun;2(6):59. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.06.05. Ann Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25333034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin and Breast Cancer: Current Findings and Future Perspectives from Preclinical and Clinical Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;17(3):396. doi: 10.3390/ph17030396. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin Treatment Suppresses Melanoma Cell Growth and Motility Through Modulation of microRNA Expression.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Feb 11;11(2):209. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020209. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30754729 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin suppresses lung adenocarcinoma by downregulating long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) AFAP1-AS1 and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) while upregulating miR-3163.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):11987-12002. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2005981. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35603556 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin and the Liver: Unlocking the Full Therapeutic Potential.Metabolites. 2024 Mar 25;14(4):186. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040186. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38668314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of metformin inhibiting cancer invasion and migration.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Sep 15;12(9):4885-4901. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33042396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-200c affects bladder cancer angiogenesis by regulating the Akt2/mTOR/HIF-1 axis.Transl Cancer Res. 2019 Dec;8(8):2713-2724. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.10.23. Transl Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 35117029 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

