Therapeutic Effects of XPO1 Inhibition in Thymic Epithelial Tumors
- PMID: 28819023
- PMCID: PMC8170838
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1323
Therapeutic Effects of XPO1 Inhibition in Thymic Epithelial Tumors
Abstract
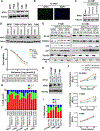
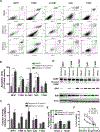
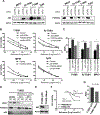
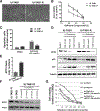
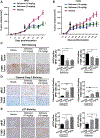
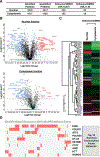
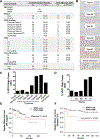
Exportin 1 (XPO1) mediates nuclear export of many cellular factors known to play critical roles in malignant processes, and selinexor (KPT-330) is the first XPO1-selective inhibitor of nuclear export compound in advanced clinical development phase for cancer treatment. We demonstrated here that inhibition of XPO1 drives nuclear accumulation of important cargo tumor suppressor proteins, including transcription factor FOXO3a and p53 in thymic epithelial tumor (TET) cells, and induces p53-dependent and -independent antitumor activity in vitro Selinexor suppressed the growth of TET xenograft tumors in athymic nude mice via inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Loss of p53 activity or amplification of XPO1 may contribute to resistance to XPO1 inhibitor in TET. Using mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis, we identified a number of proteins whose abundances in the nucleus and cytoplasm shifted significantly following selinexor treatment in the TET cells. Furthermore, we found that XPO1 was highly expressed in aggressive histotypes and advanced stages of human TET, and high XPO1 expression was associated with poorer patient survival. These results underscore an important role of XPO1 in the pathogenesis of TET and support clinical development of the XPO1 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with this type of tumors. Cancer Res; 77(20); 5614-27. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KPT-330 inhibitor of XPO1-mediated nuclear export has anti-proliferative activity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;74(3):487-95. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2495-8. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25030088 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumor activity of selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) compounds, is enhanced in non-Hodgkin lymphoma through combination with mTOR inhibitor and dexamethasone.Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 28;383(2):309-317. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27693556 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the Nuclear Export Receptor XPO1 as a Therapeutic Target for Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 15;23(6):1552-1563. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1333. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 27649553
-
Clinical Implications of Targeting XPO1-mediated Nuclear Export in Multiple Myeloma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 May;18(5):335-345. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.03.003. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018. PMID: 29610030 Review.
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport as a therapeutic target of cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Dec 5;7:85. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0085-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25476752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FOXO3a-interacting proteins' involvement in cancer: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 25;51(1):196. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09121-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38270719 Review.
-
XPO1 inhibitor KPT-330 synergizes with Bcl-xL inhibitor to induce cancer cell apoptosis by perturbing rRNA processing and Mcl-1 protein synthesis.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 21;10(6):395. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1627-9. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31113936 Free PMC article.
-
XPO1 Expression Is a Poor-Prognosis Marker in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.J Clin Med. 2019 Apr 30;8(5):596. doi: 10.3390/jcm8050596. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31052304 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation SINE Compound KPT-8602 Ameliorates Dystrophic Pathology in Zebrafish and Mouse Models of DMD.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 26;10(10):2400. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102400. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289662 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of selinexor (KPT-330), an XPO1 inhibitor, on non-hematologic cancers: a comprehensive review.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 May;149(5):2139-2155. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04247-z. Epub 2022 Aug 8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35941226 Review.
References
-
- Weinstein IB, Joe AK. Mechanisms of disease: oncogene addiction—a rationale for molecular targeting in cancer therapy. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2006;3:448–57. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Tan DS, Bedard PL, Kuruvilla J, Siu LL, Razak AR. Promising SINEs for embargoing nuclear–cytoplasmic export as an anticancer strategy. Cancer Discov 2014;4:527–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

