CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity
- PMID: 28813417
- PMCID: PMC5706633
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23643
CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity
Abstract
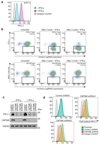
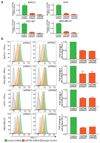
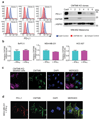
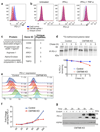
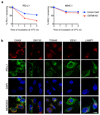
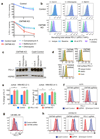
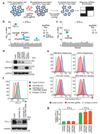
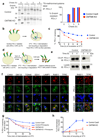
Cancer cells exploit the expression of the programmed death-1 (PD-1) ligand 1 (PD-L1) to subvert T-cell-mediated immunosurveillance. The success of therapies that disrupt PD-L1-mediated tumour tolerance has highlighted the need to understand the molecular regulation of PD-L1 expression. Here we identify the uncharacterized protein CMTM6 as a critical regulator of PD-L1 in a broad range of cancer cells, by using a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen. CMTM6 is a ubiquitously expressed protein that binds PD-L1 and maintains its cell surface expression. CMTM6 is not required for PD-L1 maturation but co-localizes with PD-L1 at the plasma membrane and in recycling endosomes, where it prevents PD-L1 from being targeted for lysosome-mediated degradation. Using a quantitative approach to profile the entire plasma membrane proteome, we find that CMTM6 displays specificity for PD-L1. Notably, CMTM6 depletion decreases PD-L1 without compromising cell surface expression of MHC class I. CMTM6 depletion, via the reduction of PD-L1, significantly alleviates the suppression of tumour-specific T cell activity in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide insights into the biology of PD-L1 regulation, identify a previously unrecognized master regulator of this critical immune checkpoint and highlight a potential therapeutic target to overcome immune evasion by tumour cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures





Comment in
-
Novel regulators of PD-L1 expression in cancer: CMTM6 and CMTM4-a new avenue to enhance the therapeutic benefits of immune checkpoint inhibitors.Ann Transl Med. 2017 Dec;5(23):467. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.09.32. Ann Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29285500 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
CMTM6 stabilizes PD-L1 expression and refines its prognostic value in tumors.Ann Transl Med. 2018 Feb;6(3):54. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.11.26. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29610746 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
CMTM6, a potential immunotherapy target.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Jan;148(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03835-9. Epub 2021 Nov 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34783871 Review.
-
Identification of CMTM6 and CMTM4 as PD-L1 protein regulators.Nature. 2017 Sep 7;549(7670):106-110. doi: 10.1038/nature23669. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28813410 Free PMC article.
-
Hsc70 promotes anti-tumor immunity by targeting PD-L1 for lysosomal degradation.Nat Commun. 2024 May 18;15(1):4237. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48597-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38762492 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of stable membranal CMTM6-PD-L1 full-length complex to evaluate the PD-1/PD-L1-CMTM6 interaction and develop anti-tumor anti-CMTM6 nanobody.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 May;44(5):1095-1104. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-01020-3. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 36418428 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of PD-L1: a novel role of pro-survival signalling in cancer.Ann Oncol. 2016 Mar;27(3):409-16. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv615. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26681673 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of a CD8+ T Cell Infiltration-Related Signature for Melanoma Patients.Front Immunol. 2021 May 10;12:659444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.659444. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34040608 Free PMC article.
-
eIF5B drives integrated stress response-dependent translation of PD-L1 in lung cancer.Nat Cancer. 2020 May;1(5):533-545. doi: 10.1038/s43018-020-0056-0. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Nat Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32984844 Free PMC article.
-
Novel targets for immunotherapy associated with exhausted CD8 + T cells in cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 May;149(5):2243-2258. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04326-1. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36107246 Review.
-
Targeting Nuclear Receptor Coactivator SRC-1 Prevents Colorectal Cancer Immune Escape by Reducing Transcription and Protein Stability of PD-L1.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(33):e2310037. doi: 10.1002/advs.202310037. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38953362 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Immune Microenvironmental Landscape of Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Immune Cell Infiltration.Dis Markers. 2022 Nov 11;2022:2361507. doi: 10.1155/2022/2361507. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36411824 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

