ADP-ribosyl-N₃: A Versatile Precursor for Divergent Syntheses of ADP-ribosylated Compounds
- PMID: 28805740
- PMCID: PMC6152188
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22081346
ADP-ribosyl-N₃: A Versatile Precursor for Divergent Syntheses of ADP-ribosylated Compounds
Abstract
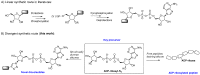
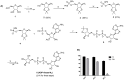
Adenosine diphosphate-ribose (ADP-ribose) and its derivatives play important roles in a series of complex physiological procedures. The design and synthesis of artificial ADP-ribosylated compounds is an efficient way to develop valuable chemical biology tools and discover new drug candidates. However, the synthesis of ADP-ribosylated compounds is currently difficult due to structural complexity, easily broken pyrophosphate bond and high hydrophilicity. In this paper, ADP-ribosyl-N₃ was designed and synthesized for the first time. With ADP-ribosyl-N₃ as the key precursor, a divergent post-modification strategy was developed to prepare structurally diverse ADP-ribosylated compounds including novel nucleotides and peptides bearing ADP-ribosyl moieties.
Keywords: ADP-ribosylated compounds; divergent synthesis; nucleotides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
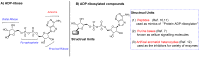

Similar articles
-
Biomimetic α-selective ribosylation enables two-step modular synthesis of biologically important ADP-ribosylated peptides.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 5;11(1):5600. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19409-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33154359 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical ADP-ribosylation: mono-ADPr-peptides and oligo-ADP-ribose.Org Biomol Chem. 2019 Jun 5;17(22):5460-5474. doi: 10.1039/c9ob00501c. Org Biomol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31112180 Review.
-
Synthesis of mono-ADP-ribosylated oligopeptides using ribosylated amino acid building blocks.J Am Chem Soc. 2010 Apr 14;132(14):5236-40. doi: 10.1021/ja910940q. J Am Chem Soc. 2010. PMID: 20232863
-
Gas-Phase Fragmentation of ADP-Ribosylated Peptides: Arginine-Specific Side-Chain Losses and Their Implication in Database Searches.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan 6;32(1):157-168. doi: 10.1021/jasms.0c00040. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33140951
-
Identification and analysis of ADP-ribosylated proteins.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;384:33-50. doi: 10.1007/82_2014_424. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25113886 Review.
Cited by
-
Four of a Kind: A Complete Collection of ADP-Ribosylated Histidine Isosteres Using Cu(I)- and Ru(II)-Catalyzed Click Chemistry.J Org Chem. 2023 Aug 4;88(15):10801-10809. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.3c00827. Epub 2023 Jul 18. J Org Chem. 2023. PMID: 37464783 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical synthesis of linear ADP-ribose oligomers up to pentamer and their binding to the oncogenic helicase ALC1.Chem Sci. 2021 Aug 18;12(37):12468-12475. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02340c. eCollection 2021 Sep 29. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34603678 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic α-selective ribosylation enables two-step modular synthesis of biologically important ADP-ribosylated peptides.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 5;11(1):5600. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19409-1. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33154359 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine ADP-Ribosylation: Chemical Synthesis of Post-Translationally Modified Ubiquitin Proteins.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Nov 16;144(45):20582-20589. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c06249. Epub 2022 Nov 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36318515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao X., Allison D., Condon B., Zhang F., Gheyi T., Zhang A., Ashok S., Russell M., MacEwan I., Qian Y., et al. The 2.5 angstrom crystal structure of the SIRT1 catalytic domain bound to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD(+)) and an indole (EX527 Analogue) reveals a novel mechanism of histone deacetylase inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2013;56:963–969. doi: 10.1021/jm301431y. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

