Melatonin ameliorates hypoglycemic stress-induced brain endothelial tight junction injury by inhibiting protein nitration of TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
- PMID: 28776759
- PMCID: PMC5656838
- DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12440
Melatonin ameliorates hypoglycemic stress-induced brain endothelial tight junction injury by inhibiting protein nitration of TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator
Abstract
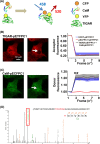
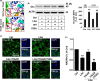
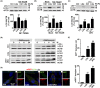
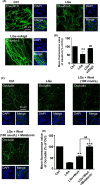
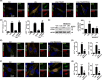
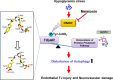
Severe hypoglycemia has a detrimental impact on the cerebrovasculature, but the molecular events that lead to the disruption of the integrity of the tight junctions remain unclear. Here, we report that the microvessel integrity was dramatically compromised (59.41% of wild-type mice) in TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) transgenic mice stressed by hypoglycemia. Melatonin, a potent antioxidant, protects against hypoglycemic stress-induced brain endothelial tight junction injury in the dosage of 400 nmol/L in vitro. FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) imaging data of endothelial cells stressed by low glucose revealed that TIGAR couples with calmodulin to promote TIGAR tyrosine nitration. A tyrosine 92 mutation interferes with the TIGAR-dependent NADPH generation (55.60% decreased) and abolishes its protective effect on tight junctions in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. We further demonstrate that the low-glucose-induced disruption of occludin and Caludin5 as well as activation of autophagy was abrogated by melatonin-mediated blockade of nitrosative stress in vitro. Collectively, we provide information on the detailed molecular mechanisms for the protective actions of melatonin on brain endothelial tight junctions and suggest that this indole has translational potential for severe hypoglycemia-induced neurovascular damage.
Keywords: TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; autophagy; hypoglycemic stress; melatonin; neurovascular; tight junctions.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Pineal Research Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ischemic injury promotes Keap1 nitration and disturbance of antioxidative responses in endothelial cells: a potential vasoprotective effect of melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2013 Apr;54(3):271-81. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12009. Epub 2012 Sep 4. J Pineal Res. 2013. PMID: 22946793
-
Inhibitory effect of melatonin on cerebral endothelial cells dysfunction induced by methamphetamine via NADPH oxidase-2.Brain Res. 2016 Nov 1;1650:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.08.045. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27590720
-
Inhibition of Rho-kinase protects cerebral barrier from ischaemia-evoked injury through modulations of endothelial cell oxidative stress and tight junctions.J Neurochem. 2014 Jun;129(5):816-26. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12681. Epub 2014 Mar 18. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24528233
-
Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep 1;315(3):C343-C356. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29949404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolonged melatonin treatment promote testicular recovery by enhancing RAC1-mediated apoptotic cell clearance and cell junction-dependent spermatogensis after heat stress.Theriogenology. 2021 Mar 1;162:22-31. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Theriogenology. 2021. PMID: 33418161 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin ameliorates microvessel abnormalities in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Apr;16(4):757-764. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.295349. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33063739 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial TFEB signaling-mediated autophagic disturbance initiates microglial activation and cognitive dysfunction.Autophagy. 2023 Jun;19(6):1803-1820. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2162244. Epub 2023 Jan 1. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36588318 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin synergistically enhances docetaxel induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to promote apoptosis by suppressing NF-κB activation in cervical cancer.Med Oncol. 2023 Jul 3;40(8):219. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02087-6. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37395921
-
Novel Multi-Antioxidant Approach for Ischemic Stroke Therapy Targeting the Role of Oxidative Stress.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 23;12(3):501. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030501. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-of-the-art: functional fluorescent probes for bioimaging and pharmacological research.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Jun;40(6):717-723. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0190-8. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 30487651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quaegebeur A, Lange C, Carmeliet P. The neurovascular link in health and disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neuron. 2011;71:406‐424. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, et al. Structure and function of the blood‐brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37:13‐25. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso FL, Brites D, Brito MA. Looking at the blood‐brain barrier: molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev. 2010;64:328‐363. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

