Transcriptome-Based Modeling Reveals that Oxidative Stress Induces Modulation of the AtfA-Dependent Signaling Networks in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 28770220
- PMCID: PMC5523550
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/6923849
Transcriptome-Based Modeling Reveals that Oxidative Stress Induces Modulation of the AtfA-Dependent Signaling Networks in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
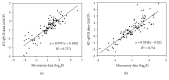
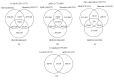
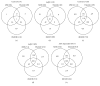
To better understand the molecular functions of the master stress-response regulator AtfA in Aspergillus nidulans, transcriptomic analyses of the atfA null mutant and the appropriate control strains exposed to menadione sodium bisulfite- (MSB-), t-butylhydroperoxide- and diamide-induced oxidative stresses were performed. Several elements of oxidative stress response were differentially expressed. Many of them, including the downregulation of the mitotic cell cycle, as the MSB stress-specific upregulation of FeS cluster assembly and the MSB stress-specific downregulation of nitrate reduction, tricarboxylic acid cycle, and ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport, showed AtfA dependence. To elucidate the potential global regulatory role of AtfA governing expression of a high number of genes with very versatile biological functions, we devised a model based on the comprehensive transcriptomic data. Our model suggests that an important function of AtfA is to modulate the transduction of stress signals. Although it may regulate directly only a limited number of genes, these include elements of the signaling network, for example, members of the two-component signal transduction systems. AtfA acts in a stress-specific manner, which may increase further the number and diversity of AtfA-dependent genes. Our model sheds light on the versatility of the physiological functions of AtfA and its orthologs in fungi.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Analyses of the AtfA/AtfB-Mediated Menadione Stress Response in Aspergillus nidulans.Cells. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):463. doi: 10.3390/cells12030463. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766807 Free PMC article.
-
Core oxidative stress response in Aspergillus nidulans.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jun 27;16(1):478. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1705-z. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26115917 Free PMC article.
-
AtfA-Independent Adaptation to the Toxic Heavy Metal Cadmium in Aspergillus nidulans.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 2;9(7):1433. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071433. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34361869 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging.Exp Gerontol. 2001 Sep;36(9):1539-50. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(01)00139-5. Exp Gerontol. 2001. PMID: 11525876 Review.
-
Regulation and Role of Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Cellular Proliferation.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 12. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 12. PMID: 30299656 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
The bZIP transcription factor ATF1 regulates blue light and oxidative stress responses in Trichoderma guizhouense.mLife. 2023 Dec 4;2(4):365-377. doi: 10.1002/mlf2.12089. eCollection 2023 Dec. mLife. 2023. PMID: 38818272 Free PMC article.
-
FvatfA regulates growth, stress tolerance as well as mycotoxin and pigment productions in Fusarium verticillioides.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Sep;104(18):7879-7899. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10717-6. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32719911 Free PMC article.
-
Global Transcriptomic Changes Elicited by sodB Deletion and Menadione Exposure in Aspergillus nidulans.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;9(11):1060. doi: 10.3390/jof9111060. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998866 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Analyses of the AtfA/AtfB-Mediated Menadione Stress Response in Aspergillus nidulans.Cells. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):463. doi: 10.3390/cells12030463. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766807 Free PMC article.
-
Growth study under combined effects of temperature, pH and salinity and transcriptome analysis revealed adaptations of Aspergillus terreus NTOU4989 to the extreme conditions at Kueishan Island Hydrothermal Vent Field, Taiwan.PLoS One. 2020 May 26;15(5):e0233621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233621. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32453769 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

