Central catalytic domain of BRAP (RNF52) recognizes the types of ubiquitin chains and utilizes oligo-ubiquitin for ubiquitylation
- PMID: 28768733
- PMCID: PMC5628404
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20161104
Central catalytic domain of BRAP (RNF52) recognizes the types of ubiquitin chains and utilizes oligo-ubiquitin for ubiquitylation
Abstract
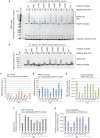
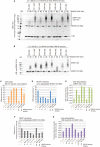
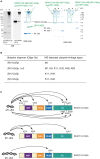
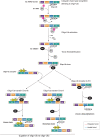
Really interesting new gene (RING)-finger protein 52 (RNF52), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, is found in eukaryotes from yeast to humans. Human RNF52 is known as breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein (BRCA1)-associated protein 2 (BRAP or BRAP2). The central catalytic domain of BRAP comprises four subdomains: nucleotide-binding α/β plait (NBP), really interesting new gene (RING) zinc finger, ubiquitin-specific protease (UBP)-like zinc finger (ZfUBP), and coiled-coil (CC). This domain architecture is conserved in RNF52 orthologs; however, the domain's function in the ubiquitin system has not been delineated. In the present study, we discovered that the RNF52 domain, comprising NBP-RING-ZfUBP-CC, binds to ubiquitin chains (oligo-ubiquitin) but not to the ubiquitin monomers, and can utilize various ubiquitin chains for ubiquitylation and auto-ubiquitylation. The RNF52 domain preferentially bound to M1- and K63-linked di-ubiquitin chains, weakly to K27-linked chains, but not to K6-, K11-, or K48-linked chains. The binding preferences of the RNF52 domain for ubiquitin-linkage types corresponded to ubiquitin usage in the ubiquitylation reaction, except for K11-, K29-, and K33-linked chains. Additionally, the RNF52 domain directly ligated the intact M1-linked, tri-, and tetra-ubiquitin chains and recognized the structural alterations caused by the phosphomimetic mutation of these ubiquitin chains. Full-length BRAP had nearly the same specificity for the ubiquitin-chain types as the RNF52 domain alone. Mass spectrometry analysis of oligomeric ubiquitylation products, mediated by the RNF52 domain, revealed that the ubiquitin-linkage types and auto-ubiquitylation sites depend on the length of ubiquitin chains. Here, we propose a model for the oligomeric ubiquitylation process, controlled by the RNF52 domain, which is not a sequential assembly process involving monomers.
Keywords: BRAP; RNF52; ubiquitin ligases; ubiquitin oligomer; ubiquitin system; ubiquitin-chain assembly.
© 2017 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Assembly and specific recognition of k29- and k33-linked polyubiquitin.Mol Cell. 2015 Apr 2;58(1):95-109. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.042. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25752577 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a HOIP/E2~ubiquitin complex reveals RBR E3 ligase mechanism and regulation.Nature. 2016 Jan 28;529(7587):546-50. doi: 10.1038/nature16511. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26789245 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into the function of RING finger (RNF)-containing proteins hRNF8 and hRNF168 in Ubc13/Mms2-dependent ubiquitylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23900-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.359653. Epub 2012 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22589545 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical Ubiquitination and Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;23(7):3705. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073705. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RINGs hold the key to ubiquitin transfer.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 Feb;37(2):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.11.001. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22154517 Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptation of Proteasomes and Lysosomes to Cellular Environments.Cells. 2020 Oct 1;9(10):2221. doi: 10.3390/cells9102221. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33019542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brap regulates liver morphology and hepatocyte turnover via modulation of the Hippo pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 May 3;119(18):e2201859119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201859119. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35476518 Free PMC article.
-
CUX2, BRAP and ALDH2 are associated with metabolic traits in people with excessive alcohol consumption.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 22;10(1):18118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75199-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33093602 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-associated protein inhibits glioma cell proliferation and migration and glioma stem cell self-renewal via the TGF-β/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Apr;43(2):223-235. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00482-8. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31776938
-
Mutation of PTPN11 (Encoding SHP-2) Promotes MEK Activation and Malignant Progression in Neurofibromin-Deficient Cells in a Manner Sensitive to BRAP Mutation.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 12;14(10):2377. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102377. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625983 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

