Recent Advances in the Inhibition of p38 MAPK as a Potential Strategy for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 28767069
- PMCID: PMC6152076
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22081287
Recent Advances in the Inhibition of p38 MAPK as a Potential Strategy for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
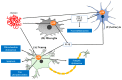
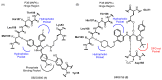
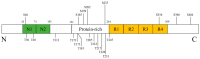
P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is a crucial target for chronic inflammatory diseases. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, as well as neurodegeneration, and there is no known cure. Recent studies on the underlying biology of AD in cellular and animal models have indicated that p38 MAPK is capable of orchestrating diverse events related to AD, such as tau phosphorylation, neurotoxicity, neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction. Thus, the inhibition of p38 MAPK is considered a promising strategy for the treatment of AD. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the targeting of p38 MAPK as a potential strategy for the treatment of AD and envision possibilities of p38 MAPK inhibitors as a fundamental therapeutics for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid beta; kinase inhibitor; neuroinflammation; p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK); tau phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
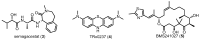
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK-P), protein kinase of 38 kDa (p38-P), stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK/JNK-P), and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaM kinase II) are differentially expressed in tau deposits in neurons and glial cells in tauopathies.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2001;108(12):1397-415. doi: 10.1007/s007020100016. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2001. PMID: 11810404
-
Targeting p38 MAPK pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2010 Mar;58(3):561-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.11.010. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Neuropharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19951717 Review.
-
Interleukin-1 promotion of MAPK-p38 overexpression in experimental animals and in Alzheimer's disease: potential significance for tau protein phosphorylation.Neurochem Int. 2001 Nov-Dec;39(5-6):341-8. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(01)00041-9. Neurochem Int. 2001. PMID: 11578769 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1 mediates pathological effects of microglia on tau phosphorylation and on synaptophysin synthesis in cortical neurons through a p38-MAPK pathway.J Neurosci. 2003 Mar 1;23(5):1605-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-05-01605.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12629164 Free PMC article.
-
The PKR/P38/RIPK1 Signaling Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 19;22(6):3136. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063136. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Serum miRNAs in Alzheimer's Disease.Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2021 Jan-Dec;36:15333175211021712. doi: 10.1177/15333175211021712. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen. 2021. PMID: 34080437 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting brain-regional gene regulatory networks from multi-omics for Alzheimer's disease phenotypes and Covid-19 severity.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 May 18;32(11):1797-1813. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddad009. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36648426 Free PMC article.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Reveal the Underlying Mechanisms of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. On the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 16;2019:8706589. doi: 10.1155/2019/8706589. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31827565 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis Reveals SH3TC2 as an Oncogene for Colorectal Cancer and Promotes Tumorigenesis via the MAPK Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 31;14(15):3735. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153735. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954399 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Expression Analysis of microRNAs and Proteins in Brain of Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Cells. 2022 Jan 4;11(1):163. doi: 10.3390/cells11010163. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011725 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

