A short D-enantiomeric antimicrobial peptide with potent immunomodulatory and antibiofilm activity against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 28761101
- PMCID: PMC5537347
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07440-0
A short D-enantiomeric antimicrobial peptide with potent immunomodulatory and antibiofilm activity against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
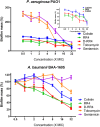
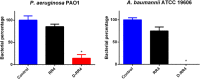
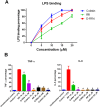
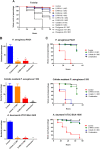
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) represent a promising therapeutic alternative for the treatment of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. The present study investigates the antimicrobial activity of new, rationally-designed derivatives of a short α-helical peptide, RR. From the peptides designed, RR4 and its D-enantiomer, D-RR4, emerged as the most potent analogues with a more than 32-fold improvement in antimicrobial activity observed against multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii. Remarkably, D-RR4 demonstrated potent activity against colistin-resistant strains of P. aeruginosa (isolated from cystic fibrosis patients) indicating a potential therapeutic advantage of this peptide over several AMPs. In contrast to many natural AMPs, D-RR4 retained its activity under challenging physiological conditions (high salts, serum, and acidic pH). Furthermore, D-RR4 was more capable of disrupting P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii biofilms when compared to conventional antibiotics. Of note, D-RR4 was able to bind to lipopolysaccharide to reduce the endotoxin-induced proinflammatory cytokine response in macrophages. Finally, D-RR4 protected Caenorhabditis elegans from lethal infections of P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii and enhanced the activity of colistin in vivo against colistin-resistant P. aeruginosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Properties and Efficacy of LL-37 Fragment GF-17D3 and Scolopendin A2 Peptides Against Resistant Clinical Strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii In Vitro and In Vivo Model Studies.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Jun;16(3):796-814. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10070-w. Epub 2023 May 6. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 37148452
-
In vitro activities of non-traditional antimicrobials alone or in combination against multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from intensive care units.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006 Mar;27(3):224-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.10.012. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006. PMID: 16464562
-
Synergistic activity profile of an antimicrobial peptide against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant strains of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens.J Pept Sci. 2017 Apr;23(4):329-333. doi: 10.1002/psc.2978. Epub 2017 Feb 8. J Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 28176481
-
Update on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii infections in the healthcare setting.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005 Aug;18(4):306-13. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000171920.44809.f0. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15985826 Review.
-
Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: resistance mechanisms and implications for therapy.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010 Jan;8(1):71-93. doi: 10.1586/eri.09.108. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010. PMID: 20014903 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Mechanismic Studies of Lactophoricin Analog, Novel Antibacterial Peptide.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;22(7):3734. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073734. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918526 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial mechanism of peptide Cec4 against Acinetobacter baumannii.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Aug 5;12:2417-2428. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S214057. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31496754 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Activities of Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics in Combating Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Oct 6;12(10):1518. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12101518. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiofilm Peptides and Peptidomimetics with Focus on Surface Immobilization.Biomolecules. 2018 May 16;8(2):27. doi: 10.3390/biom8020027. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 29772735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel D-form of hybrid peptide (D-AP19) rapidly kills Acinetobacter baumannii while tolerating proteolytic enzymes.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 23;12(1):15852. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20236-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36151303 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

