Intraflagellar transport velocity is governed by the number of active KIF17 and KIF3AB motors and their motility properties under load
- PMID: 28761002
- PMCID: PMC5565462
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1708157114
Intraflagellar transport velocity is governed by the number of active KIF17 and KIF3AB motors and their motility properties under load
Abstract
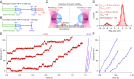
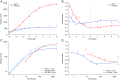
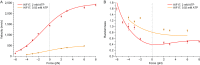
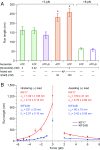
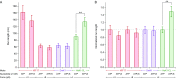
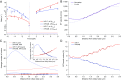
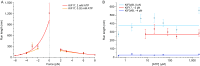
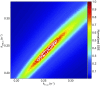
Homodimeric KIF17 and heterotrimeric KIF3AB are processive, kinesin-2 family motors that act jointly to carry out anterograde intraflagellar transport (IFT), ferrying cargo along microtubules (MTs) toward the tips of cilia. How IFT trains attain speeds that exceed the unloaded rate of the slower, KIF3AB motor remains unknown. By characterizing the motility properties of kinesin-2 motors as a function of load we find that the increase in KIF3AB velocity, elicited by forward loads from KIF17 motors, cannot alone account for the speed of IFT trains in vivo. Instead, higher IFT velocities arise from an increased likelihood that KIF3AB motors dissociate from the MT, resulting in transport by KIF17 motors alone, unencumbered by opposition from KIF3AB. The rate of transport is therefore set by an equilibrium between a faster state, where only KIF17 motors move the train, and a slower state, where at least one KIF3AB motor on the train remains active in transport. The more frequently the faster state is accessed, the higher the overall velocity of the IFT train. We conclude that IFT velocity is governed by (i) the absolute numbers of each motor type on a given train, (ii) how prone KIF3AB is to dissociation from MTs relative to KIF17, and (iii) how prone both motors are to dissociation relative to binding MTs.
Keywords: kinesin; molecular motors; optical trap; optical tweezers; single-molecule biophysics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional differentiation of cooperating kinesin-2 motors orchestrates cargo import and transport in C. elegans cilia.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;17(12):1536-45. doi: 10.1038/ncb3263. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26523365
-
Mechanism of transport of IFT particles in C. elegans cilia by the concerted action of kinesin-II and OSM-3 motors.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 25;174(7):1035-45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200606003. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17000880 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport: mechanisms of motor action, cooperation, and cargo delivery.FEBS J. 2017 Sep;284(18):2905-2931. doi: 10.1111/febs.14068. Epub 2017 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28342295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structural basis of intraflagellar transport at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2021 Jun 15;134(12):jcs247163. doi: 10.1242/jcs.247163. Epub 2021 Jun 17. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34137439
-
Intraflagellar transport motors in cilia: moving along the cell's antenna.J Cell Biol. 2008 Jan 14;180(1):23-9. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200709133. Epub 2008 Jan 7. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18180368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and regulation of kinesin motors.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Oct 11. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00780-6. Online ahead of print. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39394463 Review.
-
Cilium structure, assembly, and disassembly regulated by the cytoskeleton.Biochem J. 2018 Jul 31;475(14):2329-2353. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170453. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30064990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Regulation in Intraflagellar Transport.Cells. 2022 Sep 2;11(17):2737. doi: 10.3390/cells11172737. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraflagellar transport trains and motors: Insights from structure.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov;107:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.05.021. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32684327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular cargo transport by single-headed kinesin motors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Mar 26;116(13):6152-6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817924116. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30850543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirokawa N, Noda Y, Tanaka Y, Niwa S. Kinesin superfamily motor proteins and intracellular transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10:682–696. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N, Niwa S, Tanaka Y. Molecular motors in neurons: Transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease. Neuron. 2010;68:610–638. - PubMed
-
- Hirokawa N, Tanaka Y. Kinesin superfamily proteins (KIFs): Various functions and their relevance for important phenomena in life and diseases. Exp Cell Res. 2015;334:16–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

