Nilotinib-induced vasculopathy: identification of vascular endothelial cells as a primary target site
- PMID: 28757617
- PMCID: PMC5669463
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.245
Nilotinib-induced vasculopathy: identification of vascular endothelial cells as a primary target site
Abstract
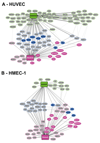
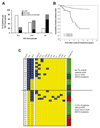
The BCR/ABL1 inhibitor Nilotinib is increasingly used to treat patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Although otherwise well-tolerated, Nilotinib has been associated with the occurrence of progressive arterial occlusive disease (AOD). Our objective was to determine the exact frequency of AOD and examine in vitro and in vivo effects of Nilotinib and Imatinib on endothelial cells to explain AOD-development. In contrast to Imatinib, Nilotinib was found to upregulate pro-atherogenic adhesion-proteins (ICAM-1, E-selectin, VCAM-1) on human endothelial cells. Nilotinib also suppressed endothelial cell proliferation, migration and tube-formation and bound to a distinct set of target-kinases, relevant to angiogenesis and atherosclerosis, including angiopoietin receptor-1 TEK, ABL-2, JAK1 and MAP-kinases. Nilotinib and siRNA against ABL-2 also suppressed KDR expression. In addition, Nilotinib augmented atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice and blocked reperfusion and angiogenesis in a hindlimb-ischemia model of arterial occlusion, whereas Imatinib showed no comparable effects. Clinically overt AOD-events were found to accumulate over time in Nilotinib-treated patients. After a median observation-time of 2.0 years, the AOD-frequency was higher in these patients (29.4%) compared to risk factor- and age-matched controls (<5%). Together, Nilotinib exerts direct pro-atherogenic and anti-angiogenic effects on vascular endothelial cells, which may contribute to development of AOD in patients with CML.
Conflict of interest statement
E.H. received honoraria from Novartis. G.H.S. received honoraria from Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Elli Lilly, Merck, Novo-Nordisk, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Aventis. D.W. received honoraria from Pfizer, BMS, Novartis, and Ariad and Research Grants from Pfizer and Ariad. R.K. received honoraria from Ariad and a Research Grant from Ariad. G.H. received honoraria form Novartis and Ariad. P.V. received honoraria from Novartis, Celgene, Pfizer, Deciphera, BMS, Ariad, and Incyte; and research grants from Novartis, Deciphera, and Ariad. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
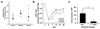
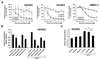
Similar articles
-
Progressive peripheral arterial occlusive disease and other vascular events during nilotinib therapy in CML.Am J Hematol. 2011 Jul;86(7):533-9. doi: 10.1002/ajh.22037. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Am J Hematol. 2011. PMID: 21538470 Clinical Trial.
-
Bosutinib, dasatinib, imatinib, nilotinib, and ponatinib differentially affect the vascular molecular pathways and functionality of human endothelial cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jan;60(1):189-199. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1466294. Epub 2018 May 9. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019. PMID: 29741440
-
Nilotinib versus imatinib for the treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, chronic myeloid leukaemia: 24-month minimum follow-up of the phase 3 randomised ENESTnd trial.Lancet Oncol. 2011 Sep;12(9):841-51. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70201-7. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Lancet Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21856226 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of arterial and venous occlusive events in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with new generation BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Jan;16(1):5-12. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1261824. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 27852118 Review.
-
Nilotinib: a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia.Clin Ther. 2008 Nov;30(11):1956-75. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.11.014. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 19108785 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelium as a Source of Cardiovascular Toxicity From Antitumor Kinase Inhibitors.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024 Oct;44(10):2143-2153. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.319864. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024. PMID: 39145393 Review.
-
Cardiovascular events in CML patients treated with Nilotinib: validation of the HFA-ICOS baseline risk score.Cardiooncology. 2024 Jul 15;10(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40959-024-00245-x. Cardiooncology. 2024. PMID: 39010172 Free PMC article.
-
The BCR::ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors ponatinib and nilotinib differentially affect endothelial angiogenesis and signalling.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul 15. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05070-5. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39009935
-
Cardiovascular Toxicity of Antineoplastic Treatments in Hematological Diseases: Focus on Molecular Mechanisms to Improve Therapeutic Management.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 9;13(6):1574. doi: 10.3390/jcm13061574. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38541800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nilotinib-induced alterations in endothelial cell function recapitulate clinical vascular phenotypes independent of ABL1.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 26;14(1):7123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57686-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38532120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O'Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM. The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:164–172. - PubMed
-
- Rowley JD. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973;243:290–293. - PubMed
-
- Sattler M, Griffin JD. Molecular mechanisms of transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Semin Hematol. 2003;40:4–10. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ. Inhibition of the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic strategy for CML. Oncogene. 2002;21:8541–8546. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:994–1004. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

