Genome-wide Single-Molecule Footprinting Reveals High RNA Polymerase II Turnover at Paused Promoters
- PMID: 28735898
- PMCID: PMC5548954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.027
Genome-wide Single-Molecule Footprinting Reveals High RNA Polymerase II Turnover at Paused Promoters
Abstract
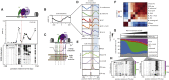
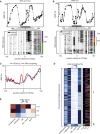
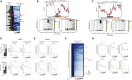
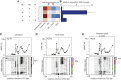
Transcription initiation entails chromatin opening followed by pre-initiation complex formation and RNA polymerase II recruitment. Subsequent polymerase elongation requires additional signals, resulting in increased residence time downstream of the start site, a phenomenon referred to as pausing. Here, we harnessed single-molecule footprinting to quantify distinct steps of initiation in vivo throughout the Drosophila genome. This identifies the impact of promoter structure on initiation dynamics in relation to nucleosomal occupancy. Additionally, perturbation of transcriptional initiation reveals an unexpectedly high turnover of polymerases at paused promoters-an observation confirmed at the level of nascent RNAs. These observations argue that absence of elongation is largely caused by premature termination rather than by stable polymerase stalling. In support of this non-processive model, we observe that induction of the paused heat shock promoter depends on continuous initiation. Our study provides a framework to quantify protein binding at single-molecule resolution and refines concepts of transcriptional pausing.
Keywords: DNA footprinting; GTF; TBP; genomics; single molecule; transcription; transcriptional pausing.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Kinetics of promoter Pol II on Hsp70 reveal stable pausing and key insights into its regulation.Genes Dev. 2014 Jan 1;28(1):14-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.231886.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24395245 Free PMC article.
-
Paused RNA polymerase II inhibits new transcriptional initiation.Nat Genet. 2017 Jul;49(7):1045-1051. doi: 10.1038/ng.3867. Epub 2017 May 15. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28504701
-
Analyses of promoter-proximal pausing by RNA polymerase II on the hsp70 heat shock gene promoter in a Drosophila nuclear extract.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):5433-43. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.10.5433. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8816456 Free PMC article.
-
The heat shock response: A case study of chromatin dynamics in gene regulation.Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;91(1):42-8. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2012-0075. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23442140 Review.
-
Pause & go: from the discovery of RNA polymerase pausing to its functional implications.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;46:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28363125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin accessibility profiling methods.Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2021;1:10. doi: 10.1038/s43586-020-00008-9. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2021. PMID: 38410680 Free PMC article.
-
Nonlinear control of transcription through enhancer-promoter interactions.Nature. 2022 Apr;604(7906):571-577. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04570-y. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35418676 Free PMC article.
-
Global analyses of the dynamics of mammalian microRNA metabolism.Genome Res. 2019 Nov;29(11):1777-1790. doi: 10.1101/gr.251421.119. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Genome Res. 2019. PMID: 31519739 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Pol II pausing facilitates phased pluripotency transitions by buffering transcription.Genes Dev. 2022 Aug 18;36(13-14):770-89. doi: 10.1101/gad.349565.122. Online ahead of print. Genes Dev. 2022. PMID: 35981753 Free PMC article.
-
P-TEFb Regulates Transcriptional Activation in Non-coding RNA Genes.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 24;10:342. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00342. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31068966 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold C.D., Gerlach D., Stelzer C., Boryń Ł.M., Rath M., Stark A. Genome-wide quantitative enhancer activity maps identified by STARR-seq. Science. 2013;339:1074–1077. - PubMed
-
- Bell O., Schwaiger M., Oakeley E.J., Lienert F., Beisel C., Stadler M.B., Schübeler D. Accessibility of the Drosophila genome discriminates PcG repression, H4K16 acetylation and replication timing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010;17:894–900. - PubMed
-
- Brannan K., Kim H., Erickson B., Glover-Cutter K., Kim S., Fong N., Kiemele L., Hansen K., Davis R., Lykke-Andersen J., Bentley D.L. mRNA decapping factors and the exonuclease Xrn2 function in widespread premature termination of RNA polymerase II transcription. Mol. Cell. 2012;46:311–324. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

