A gene network regulated by FGF signalling during ear development
- PMID: 28733657
- PMCID: PMC5522468
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-05472-0
A gene network regulated by FGF signalling during ear development
Abstract
During development cell commitment is regulated by inductive signals that are tightly controlled in time and space. In response, cells activate specific programmes, but the transcriptional circuits that maintain cell identity in a changing signalling environment are often poorly understood. Specification of inner ear progenitors is initiated by FGF signalling. Here, we establish the genetic hierarchy downstream of FGF by systematic analysis of many ear factors combined with a network inference approach. We show that FGF rapidly activates a small circuit of transcription factors forming positive feedback loops to stabilise otic progenitor identity. Our predictive network suggests that subsequently, transcriptional repressors ensure the transition of progenitors to mature otic cells, while simultaneously repressing alternative fates. Thus, we reveal the regulatory logic that initiates ear formation and highlight the hierarchical organisation of the otic gene network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
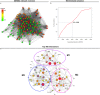
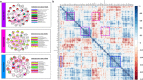
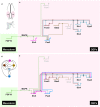

Similar articles
-
Induction of the inner ear: stepwise specification of otic fate from multipotent progenitors.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.018. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23194992 Review.
-
A systems-level approach reveals new gene regulatory modules in the developing ear.Development. 2017 Apr 15;144(8):1531-1543. doi: 10.1242/dev.148494. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Development. 2017. PMID: 28264836 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development.BMC Dev Biol. 2015 Oct 6;15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8. BMC Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26443994 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive restriction of otic fate: the role of FGF and Wnt in resolving inner ear potential.Development. 2008 Oct;135(20):3415-24. doi: 10.1242/dev.026674. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Development. 2008. PMID: 18799542
-
[Roles of the FGF signaling pathway in regulating inner ear development and hair cell regeneration].Yi Chuan. 2018 Jul 20;40(7):515-524. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-407. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 30021715 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Targeting Cellular Trafficking of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors as a Strategy for Selective Cancer Treatment.J Clin Med. 2018 Dec 20;8(1):7. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010007. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30577533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lsd1 interacts with cMyb to demethylate repressive histone marks and maintain inner ear progenitor identity.Development. 2018 Feb 21;145(4):dev160325. doi: 10.1242/dev.160325. Development. 2018. PMID: 29437831 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the periotic mesenchyme in the development of sensory cells in early mouse cochlea.J Otol. 2020 Dec;15(4):138-143. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jul 2. J Otol. 2020. PMID: 33293914 Free PMC article.
-
FOXI3 pathogenic variants cause one form of craniofacial microsomia.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):2026. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37703-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37041148 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer activation by FGF signalling during otic induction.Dev Biol. 2020 Jan 1;457(1):69-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2019.09.006. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31539539 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

