Plasma dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 activity is associated with left ventricular systolic function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 28733630
- PMCID: PMC5522492
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-06514-3
Plasma dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 activity is associated with left ventricular systolic function in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
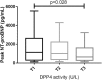
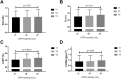
Plasma dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 activity (DPP4a) is inversely associated with left ventricular function in patients with heart failure (HF) or diabetes. However, the association between DPP4a and left ventricular function in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients has not been reported. We studied this association in 584 consecutive STEMI patients at a tertiary referral center from July 2014 to October 2015. DPP4a and plasma N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels were quantified by enzymatic assays. The median serum NT-proBNP levels were highest in patients of the lowest tertile (T1) of DPP4a compared with that of the highest tertile (T3) (p = 0.028). The STEMI patients in T1 exhibited lower left ventricular systolic function (T1 vs. T3: left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF): 50.13 ± 9.12 vs. 52.85 ± 6.82%, p = 0.001). Multivariate logistic-regression analyses (adjusted for confounding variables) showed that a 1 U/L increase in DPP4a was associated with a decreased incidence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) (adjusted odds ratio: 0.90; 95% CI: 0.87-0.94; p < 0.01). In conclusion, low DPP4a is independently associated with LVSD in STEMI patients, which suggests that DPP4 may be involved in the mechanisms of LVSD in STEMI patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of plasma DPP4 activity in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Jun 6;16(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0553-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28587613 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma DPP4 activity is associated with no-reflow and major bleeding events in Chinese PCI-treated STEMI patients.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 21;6:39412. doi: 10.1038/srep39412. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 28000723 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence and predictors of left ventricular systolic dysfunction at hospital discharge and in long-term follow-up after acute myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Kardiol Pol. 2012;70(4):329-40. Kardiol Pol. 2012. PMID: 22528703
-
Augmented glycaemic gap is a marker for an increased risk of post-infarct left ventricular systolic dysfunction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Jul 4;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01075-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32622355 Free PMC article.
-
Does Oral Beta-Blocker Therapy Improve Long-Term Survival in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction With Preserved Systolic Function? A Meta-Analysis.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016 May;21(3):280-5. doi: 10.1177/1074248415608011. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26424094 Review.
Cited by
-
A prospective randomized study comparing effects of empagliflozin to sitagliptin on cardiac fat accumulation, cardiac function, and cardiac metabolism in patients with early-stage type 2 diabetes: the ASSET study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Feb 2;20(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01228-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33530982 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reduced post-operative DPP4 activity associated with worse patient outcome after cardiac surgery.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 7;8(1):11820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30235-w. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30087386 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

