CD36 overexpression: a possible etiopathogenic mechanism of atherosclerosis in patients with prediabetes and diabetes
- PMID: 28729885
- PMCID: PMC5516302
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-017-0253-x
CD36 overexpression: a possible etiopathogenic mechanism of atherosclerosis in patients with prediabetes and diabetes
Abstract
Rationale: CD36 is a scavenger receptor located on monocytes which is involved in foam cell transformation.
Aim: To evaluate CD36 expression under different glycemic states in both healthy subjects and in atherosclerotic patients.
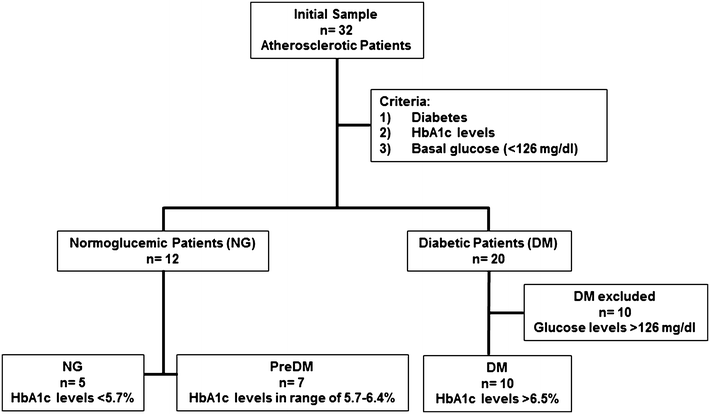
Subjects and methods: In order to evaluate the possible effects of hyperglycemia on CD36 expression in healthy subjects, an in vitro experiment was carried out using monocyte in three different conditions: extreme hyperglycemia (HG), euglycemia (EG) and in the absence of glucose. On the other hand, three groups of atherosclerotic patients were evaluated according to their glycemic conditions: normoglycemic (NG), prediabetic (preDM) and diabetic (DM) patients. CD36 expression (mRNA, non-glycated and glycated protein) was analyzed in monocytes.
Results: CD36 mRNA expression in the in vitro experiment peaked at 4 and 24 h under HG conditions. No differences in mRNA levels were found in the EG and control group. The level of non-glycated proteins was higher in HG and EG conditions compared with control group. Glycated protein expression was inhibited by glucose in a sustained manner. In atherosclerotic patients, a significant association was observed when comparing glycated CD36 protein expression in DM with NG patients (p = 0.03). No significant differences were found in mRNA and non-glycated CD36 expression in these patients. Moreover, BMI, insulin, weight and treatment were shown to be related to CD36 expression (mRNA, non-glycated and glycated protein levels, depending of the case) in atherosclerotic patients.
Conclusions: Hyperglycemia is an important modulator of CD36 mRNA and non-glycated protein expression in vitro, increasing de novo synthesis in healthy subjects. In atherosclerotic patients, there are progressive increases in CD36 receptors, which may be due to a post-translational stimulus.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; CD36 receptor; Human clinical; Monocytes; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of human monocyte CD36 by type 2 diabetes mellitus and other atherosclerotic risk factors.Eur J Clin Invest. 2011 Aug;41(8):854-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02475.x. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Eur J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21668445
-
Mechanism linking atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes: increased expression of scavenger receptor CD36 in monocytes.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Oct 20;118(20):1717-22. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16313757
-
Increased expression of a scavenger receptor (CD36) in monocytes from subjects with Type 2 diabetes.Atherosclerosis. 2003 Mar;167(1):129-34. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(02)00421-5. Atherosclerosis. 2003. PMID: 12618277
-
[Scavenger receptor CD36: its expression, regulation, and role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Part I].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:142-51. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006. PMID: 16552394 Review. Polish.
-
[The influence of diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance on receptor CD36 expression. Part II. The role of receptor CD36 in the pathomechanism of diabetes complications].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006;60:152-62. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2006. PMID: 16552395 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of cluster of differentiation 36 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlates with frailty severity in older adults.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Jun;13(3):1948-1955. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13003. Epub 2022 Apr 17. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 35434940 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial wall inflammation assessed by 18F-FDG-PET/CT is higher in individuals with Type 1 diabetes and associated with circulating inflammatory proteins.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Aug 19;119(10):1942-1951. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad058. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37079728 Free PMC article.
-
Microarray Expression Profile of Myricetin-Treated THP-1 Macrophages Exhibits Alterations in Atherosclerosis-Related Regulator Molecules and LXR/RXR Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 23;24(1):278. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010278. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613720 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Soluble CD36 is Similar in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus versus Non-Diabetic Subjects.J Clin Med. 2019 May 18;8(5):710. doi: 10.3390/jcm8050710. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31109109 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Scavenger Receptor CD36 in Accelerated Diabetic Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 5;21(19):7360. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197360. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33028031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper R, Cutler J, Desvigne-Nickens P, Fortmann SP, Friedman L, Havlik R, et al. Trends and disparities in coronary heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases in the United States: findings of the national conference on cardiovascular disease prevention. Circulation. 2000;102(25):3137–3147. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.102.25.3137. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The DECODE study group. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group Glucose tolerance and mortality: comparison of WHO and American Diabetes Association diagnostic criteria. Diabetes epidemiology: Collaborative analysis Of Diagnostic criteria in Europe. Lancet. 1999;354(9179):617–621. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12131-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

