MicroRNA-200c inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration of lung cancer by targeting HMGB1
- PMID: 28727734
- PMCID: PMC5519074
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180844
MicroRNA-200c inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and migration of lung cancer by targeting HMGB1
Abstract
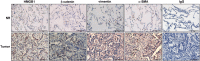
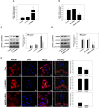
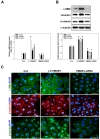
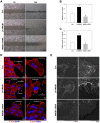
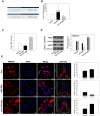
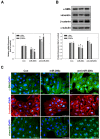
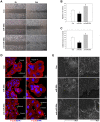
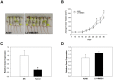
MicroRNAs (miRs) play critical roles in cancer development, proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion, and migration through regulating the expression of oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. Previous studies have indicated that miR-200c acts as a tumour suppressor in various cancers by downregulating high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and thereby suppressing EMT and metastasis. In addition, miR-200c was reported to be downregulated and correlated with poor outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its functional role in HMGB1 regulation in NSCLC is still unclear. This study aimed to clarify whether miR-200c acts as a tumour suppressor in NSCLC by downregulating HMGB1, which is associated with EMT, invasion, cytoskeleton rearrangement, and migration in vitro and in vivo. In order to demonstrate HMGB1 downregulation by miR-200c, the NSCLC cell line A549 was transfected with miR-200c mimic or inhibitor. The mimic significantly reduced HMGB1 expression and suppressed EMT, invasion, and migration, while the inhibitor generated the opposite effects. Additionally, using xenograft mouse models, we confirmed that HMGB1 overexpression increased tumour EMT. In summary, our results demonstrated that miR-200c could suppress EMT, invasion, and migration of NSCLC cells by downregulating HMGB1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-200c inhibits metastasis of breast cancer cells by targeting HMGB1.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014 Apr;34(2):201-206. doi: 10.1007/s11596-014-1259-3. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24710933
-
Long non-coding RNA linc00673 regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-150-5p.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 11;16(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0685-9. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28697764 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-suppressive effects of microRNA-181d-5p on non-small-cell lung cancer through the CDKN3-mediated Akt signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):L918-L933. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00334.2018. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30628487
-
Roles of miR-200 family members in lung cancer: more than tumor suppressors.Future Oncol. 2018 Nov;14(27):2875-2886. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0155. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30208739 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs as emerging regulators of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):36787-36799. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16375. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415568 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of anlotinib-induced autophagy attenuates invasion and migration by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cytoskeletal rearrangement through ATG5 in human osteosarcoma cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Feb 19;57:e13152. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e13152. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38381883 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of the Immune System and Molecular Cell Signaling Pathways in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 12;24(2):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021506. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Encapsulated miR-200c and Nkx2.1 in a nuclear/mitochondria transcriptional regulatory network of non-metastatic and metastatic lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 11;19(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5337-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30744585 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and therapeutic potentials of microRNAs to non-small cell lung cancer.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 14;9(11):e22080. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22080. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38058618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-145 and miR-497 suppress TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting MTDH.Cancer Cell Int. 2018 Jul 27;18:105. doi: 10.1186/s12935-018-0601-4. eCollection 2018. Cancer Cell Int. 2018. PMID: 30065618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osugi J, Muto S, Matsumura Y, Higuchi M, Suzuki H, Gotoh M. Prognostic impact of the high-sensitivity modified Glasgow prognostic score in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics. 2016;12(2):945 doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.176168 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bianchi ME, Agresti A. HMG proteins: dynamic players in gene regulation and differentiation. Current opinion in genetics & development. 2005;15(5):496–506. - PubMed
-
- Salgado J, Villalaín J, Gómez-Fernández JC. Effects of platelet-activating factor and related lipids on dielaidoylphosphatidylethanolamine by DSC, FTIR and NMR. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes. 1993;1145(2):284–92. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Xiang L, Li H, Chen P, Feng Y, Zhang J, et al. The role of HMGB1 signaling pathway in the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. International journal of molecular sciences. 2015;16(9):22527–40. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922527 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

