ErbB4 deletion accelerates renal fibrosis following renal injury
- PMID: 28724608
- PMCID: PMC6031915
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00260.2017
ErbB4 deletion accelerates renal fibrosis following renal injury
Abstract
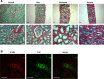
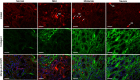
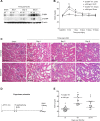
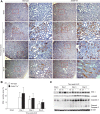
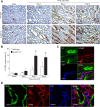
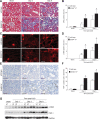
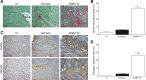
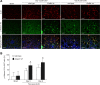
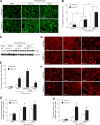
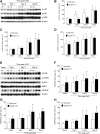
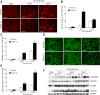
Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF) is a prominent factor in the progression of chronic kidney disease regardless of etiology. Avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4 (ErbB4) expression levels were inversely correlated to renal fibrosis in human fibrotic kidneys. In both unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) and ischemia-reperfusion injury followed by uninephrectomy (IRI/UNx) mouse models, expression levels of ErbB4 were elevated in the early stage of renal injury. Using mice with global ErbB4 deletion except for transgenic rescue in cardiac tissue ( ErbB4-/-ht+), we determined that UUO induced similar injury in proximal tubules compared with wild-type mice but more severe injury in distal nephrons. TIF was apparent earlier and was more pronounced following UUO in ErbB4-/-ht+ mice. With ErbB4 deletion, UUO injury inhibited protein kinase B phosphorylation and increased the percentage of cells in G2/M arrest. There was also increased nuclear immunostaining of yes-associated protein and increased expression of phospho-Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3, snail1, and vimentin. These results indicate that ErbB4 deletion accelerates the development and progression of renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Similar results were found in a mouse IRI/UNx model. In conclusion, increased expression of ErbB4 in the early stages of renal injury may reflect a compensatory effect to lessen tubulointerstitial injury.
Keywords: avian erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog 4; cell cycle; epithelial dedifferentiation; tubulointerstitial fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ISG15 accelerates acute kidney injury and the subsequent AKI-to-CKD transition by promoting TGFβR1 ISGylation.Theranostics. 2024 Jul 22;14(11):4536-4553. doi: 10.7150/thno.95796. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39113797 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal Tubule-Derived Amphiregulin Amplifies and Integrates Profibrotic EGF Receptor Signals in Kidney Fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Dec;30(12):2370-2383. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019030321. Epub 2019 Nov 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31676723 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer deficiency in proximal tubules exacerbates renal injury and tubulointerstitial fibrosis and upregulates Smad2/3.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):F1822-F1832. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00402.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30280598 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral ureteral obstruction: beyond obstruction.Int Urol Nephrol. 2014 Apr;46(4):765-76. doi: 10.1007/s11255-013-0520-1. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24072452 Review.
-
The Tubulointerstitial Pathophysiology of Progressive Kidney Disease.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017 Mar;24(2):107-116. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2016.11.011. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28284376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Inhibition of TRPC6 by SH045 Attenuates Renal Fibrosis in a New Zealand Obese (NZO) Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 20;23(12):6870. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126870. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743312 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and kidney injury attenuated by prior intake of Brazil nuts in the process of ischemia and reperfusion.J Bras Nefrol. 2018 Oct-Dec;40(4):312-318. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2018-0016. Epub 2018 Aug 16. J Bras Nefrol. 2018. PMID: 30118536 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between the concentrations of CD68, TGF-β1, renal injury index and prognosis in glomerular diseases.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):56. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9184. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32952646 Free PMC article.
-
Potential targeted therapy and diagnosis based on novel insight into growth factors, receptors, and downstream effectors in acute kidney injury and acute kidney injury-chronic kidney disease progression.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Feb 14;5(1):9. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0106-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32296020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Reduction in Chromatin Accessibility and Unique Transcription Factor Footprints in Endothelial Cells and Fibroblasts in Scleroderma Skin.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;73(8):1501-1513. doi: 10.1002/art.41694. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33586346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boukhalfa G, Desmoulière A, Rondeau E, Gabbiani G, Sraer JD. Relationship between alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and fibrotic changes in human kidney. Exp Nephrol 4: 241–247, 1996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

