tRNA engineering for manipulating genetic code
- PMID: 28722545
- PMCID: PMC6103704
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1343227
tRNA engineering for manipulating genetic code
Abstract
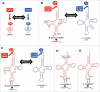
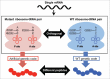
In ribosomal translation, only 20 kinds of proteinogenic amino acids (pAAs), namely 19 l-amino acids and glycine, are exclusively incorporated into polypeptide chain. To overcome this limitation, various methods to introduce non-proteinogenic amino acids (npAAs) other than the 20 pAAs have been developed to date. However, the repertoire of amino acids that can be simultaneously introduced is still limited. Moreover, the efficiency of npAA incorporation is not always sufficient depending on their structures. Fidelity of translation is sometimes low due to misincorporation of competing pAAs and/or undesired translation termination. Here, we provide an overview of efforts to solve these issues, focusing on the engineering of tRNAs.
Keywords: aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; flexizyme; genetic code reprogramming; non-proteinogenic amino acid; peptide; ribosome; tRNA; translation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome.Nature. 2010 Mar 18;464(7287):441-4. doi: 10.1038/nature08817. Epub 2010 Feb 14. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20154731
-
tRNAPyl: Structure, function, and applications.RNA Biol. 2018;15(4-5):441-452. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1356561. Epub 2017 Sep 13. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 28837402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Translation Components for Genetic Code Expansion.J Mol Biol. 2022 Apr 30;434(8):167302. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167302. Epub 2021 Oct 18. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34673113 Review.
-
Challenges of site-specific selenocysteine incorporation into proteins by Escherichia coli.RNA Biol. 2018;15(4-5):461-470. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1440876. Epub 2018 Mar 12. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 29447106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolved sequence contexts for highly efficient amber suppression with noncanonical amino acids.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Dec 19;9(12):2815-22. doi: 10.1021/cb5006273. Epub 2014 Oct 17. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25299570
Cited by
-
Evolutionary tuning impacts the design of bacterial tRNAs for the incorporation of unnatural amino acids by ribosomes.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Oct;46:138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.07.016. Epub 2018 Jul 27. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 30059836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Codon-Reduced Protein Synthesis With Manipulating tRNA Components in Cell-Free System.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 May 13;10:891808. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.891808. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35646841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing tRNAs for nonsense suppression.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 22;12(1):3850. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24076-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34158503 Free PMC article.
-
Macrocyclic Peptides Closed by a Thioether-Bipyridyl Unit That Grants Cell Membrane Permeability.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023 Aug 13;3(5):429-437. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.3c00027. eCollection 2023 Oct 18. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2023. PMID: 37876498 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering tRNAs for the Ribosomal Translation of Non-proteinogenic Monomers.Chem Rev. 2024 May 22;124(10):6444-6500. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00894. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 38688034 Review.
References
-
- Robertson SA, Noren CJ, Anthony-Cahill SJ, Griffith MC, Schultz PG. The use of 5′-phospho-2 deoxyribocytidylylriboadenosine as a facile route to chemical aminoacylation of tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17:9649-60; PMID:2602139; https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.23.9649 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murakami H, Ohta A, Ashigai H, Suga H. A highly flexible tRNA acylation method for non-natural polypeptide synthesis. Nat Methods 2006; 3:357-9; PMID:16628205; https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth877 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goto Y, Katoh T, Suga H. Flexizymes for genetic code reprogramming. Nat Protoc 2011; 6:779-90; PMID:21637198; https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.331 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Brock A, Herberich B, Schultz PG. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science 2001; 292:498-500; PMID:11313494; https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060077 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ai HW. Biochemical analysis with the expanded genetic lexicon. Anal Bioanal Chem 2012; 403:2089-102; PMID:22322380; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5784-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
