(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates myocardial injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion in diabetic rats and in H9c2 cells under hyperglycemic conditions
- PMID: 28714516
- PMCID: PMC5504977
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3014
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates myocardial injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion in diabetic rats and in H9c2 cells under hyperglycemic conditions
Abstract
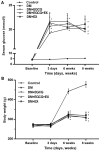
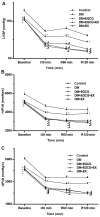
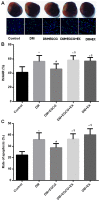
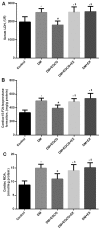
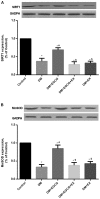
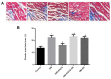
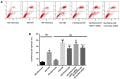
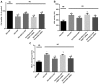
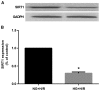
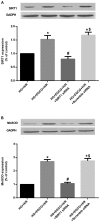
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) exerts multiple beneficial effects on cardiovascular performance. In this study, we aimed to examine the effects of EGCG on diabetic cardiomyopathy during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. EGCG (100 mg/kg/day) was administered at week 6 for 2 weeks to diabetic rats following the induction of type 1 diabetes by streptozotocin (STZ). At the end of week 8, the animals were subjected to myocardial I/R injury. The EGCG-elicited structural and functional effects were analyzed. Additionally, EGCG (20 µM) was administered for 24 h to cultured cardiac H9c2 cells under hyperglycemic conditions (30 mM glucose) prior to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) challenge, and its effects on oxidative stress were compared to H9c2 cells transfecteed with silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) small interfering RNA (siRNA). In rats with STZ-induced diabetes, EGCG treatment ameliorated post-ischemic cardiac dysfunction, decreased the myocardial infarct size, apoptosis and cardiac fibrosis, and reduced the elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and malonaldehyde (MDA) levels, and attenuated oxidative stress. Furthermore, EGCG significantly reduced H/R injury in cardiac H9c2 cells exposed to high glucose as evidenced by reduced apoptotic cell death and oxidative stress. The protein expression levels of SIRT1 and manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) were reduced in the diabetic rats and the H9c2 cells under hyperglycemic conditions, compared with the control rats following I/R injury and H9c2 cells under normal glucose conditions. EGCG pre-treatment significantly upregulated the levels of htese proteins in vitro and in vivo. However, treatment with EX527 and SIRT1 siRNA blocked the EGCG-mediated cardioprotective effects. Taken together, our data indicate that SIRT1 plays a critical role in the EGCG-mediated amelioration of I/R injury in diabetic rats, which suggests that EGCG may be a promising dietary supplement for the prevention of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced silent information regulator 1 signaling exacerbates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats and the protective effect of melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2015 Oct;59(3):376-90. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12269. Epub 2015 Sep 11. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 26327197
-
Rutin alleviates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in myocardial cells by up-regulating SIRT1 expression.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Jan 5;297:44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30365940
-
SIRT1 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating eNOS in diabetic rats.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Oct 21;14:143. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0299-8. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26489513 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the therapeutic potential of epigallocatechin-3-gallate.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:2155-2172. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.086. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551473 Review.
-
CPP-conjugated anti-apoptotic peptides as therapeutic tools of ischemia-reperfusion injuries.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(16):2970-8. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319160011. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23140457 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effects of Polyphenols against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.Molecules. 2020 Jul 30;25(15):3469. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153469. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective effect of epigallocatechin gallate in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis in preclinical animal studies.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 28;13(1):14050. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41275-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37640837 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase to mitochondria protects cells from high glucose-induced apoptosis.Endocrine. 2018 Jun;60(3):445-457. doi: 10.1007/s12020-018-1575-7. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Endocrine. 2018. PMID: 29564753
-
Catechin relieves hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardial cell apoptosis via down-regulating lncRNA MIAT.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Feb;24(3):2356-2368. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14919. Epub 2020 Jan 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31955523 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate against neuroinflammation and anxiety-like behavior in a rat model of myocardial infarction.Brain Behav. 2020 Jun;10(6):e01633. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1633. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Brain Behav. 2020. PMID: 32304289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J, Li H, Irwin MG, Xia ZY, Mao X, Lei S, Wong GT, Hung V, Cheung CW, Fang X, et al. Propofol ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction via heme oxygenase-1/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway in rats. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:e583–e594. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000415. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

