Assessment of Conflicts of Interest in Robotic Surgical Studies: Validating Author's Declarations With the Open Payments Database
- PMID: 28700443
- PMCID: PMC6003408
- DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002420
Assessment of Conflicts of Interest in Robotic Surgical Studies: Validating Author's Declarations With the Open Payments Database
Abstract
Background: Accurate conflict of interest (COI) statements are important, as a known COI may invalidate study results due to the potential risk of bias.
Objective: To determine the accuracy of self-declared COI statements in robotic studies and identify risk factors for undeclared payments.
Methods: Robotic surgery studies were identified through EMBASE and MEDLINE and included if published in 2015 and had at least one American author. Undeclared COI were determined by comparing the author's declared COI with industry reported payments found in the "Open Payments" database for 2013 and 2014. Undeclared payments and discrepancies in the COI statement were determined. Risk factors were assessed for an association with undeclared payments at the author and study level.
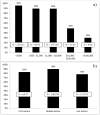
Results: A total of 458 studies (2253 authors) were included. Approximately, 240 (52%) studies had 1 or more author receive undeclared payments and included 183 where "no COI" was explicitly declared, and 57 with no declaration statement present. Moreover, 21% of studies and 18% of authors with a COI declared it so in a COI statement. Studies that had undeclared payments from Intuitive were more likely to recommend robotic surgery compared with those that declared funding (odds ratio 4.29, 95% confidence interval 2.55-7.21).
Conclusions: We found that it was common for payments from Intuitive to be undeclared in robotic surgery articles. Mechanisms for accountability in COI reporting need to be put into place by journals to achieve appropriate transparency to those reading the journal article.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Dr. Nash received reimbursement for travel from Novadaq Technologies Inc., which has a licence and development agreement with Intuitive Surgical Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Corporate Payments on Robotic Surgery Research: A Systematic Review.Ann Surg. 2019 Mar;269(3):389-396. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003000. Ann Surg. 2019. PMID: 30067545
-
Assessment of self-reported financial conflicts of interest in vascular surgery studies.J Vasc Surg. 2021 Dec;74(6):2047-2053. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2021.05.040. Epub 2021 Jun 23. J Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 34171423
-
Discrepancies in Self-Reported and Actual Conflicts of Interest for Robotic Pediatric Urological Surgery.J Urol. 2019 Feb;201(2):393-399. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.07.043. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30053509
-
The Impact of Author Financial Conflicts on Robotic-Assisted Joint Arthroplasty Research.J Arthroplasty. 2021 Apr;36(4):1462-1469. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2020.10.033. Epub 2020 Oct 26. J Arthroplasty. 2021. PMID: 33199093 Review.
-
Industry-specific Patterns in the Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest in Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery: A Review of the Nerve Allograft Industry.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022 Nov 15;30(22):1083-1089. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-22-00326. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022. PMID: 36001882 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Cancer Specific Outcomes following Minimally Invasive and Open Surgical Resection of Early Stage Kidney Cancer from a National Cancer Registry.J Urol. 2020 Jun;203(6):1094-1100. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000741. Epub 2020 Jan 8. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31913076 Free PMC article.
-
Reporting of conflicts of interest by authors of primary studies on health policy and systems research: a cross-sectional survey.BMJ Open. 2020 Jul 19;10(7):e032425. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032425. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32690493 Free PMC article.
-
Do Robotics and Virtual Reality Add Real Progress to Mirror Therapy Rehabilitation? A Scoping Review.Rehabil Res Pract. 2018 Aug 19;2018:6412318. doi: 10.1155/2018/6412318. eCollection 2018. Rehabil Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30210873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of disclosure of conflicts of interest in studies comparing robot-assisted and laparoscopic cholecystectomies-a persistent problem.Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb;37(2):1515-1527. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09440-2. Epub 2022 Jul 18. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 35851821 Review.
-
Funding has no effect on clinical outcomes of total joint arthroplasty emerging technologies: a systematic review of bibliometrics and conflicts of interest.Arthroplasty. 2022 Nov 1;4(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s42836-022-00146-3. Arthroplasty. 2022. PMID: 36316729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [Accessed November 2016];Recommendations for the Conduct, Reporting, Editing, and Publication of Scholarly Work in Medical Journals. http://icmje.org/recommendations/ - PubMed
-
- American Medical Association (AMA) [Accessed November 2016];Code of Medical Ethics, Chapter 7 Opinion on Research and Innovation. https://www.ama-assn.org/about-us/code-medical-ethics.
-
- Buerba RA, Fu MC, Grauer JN. Discrepancies in spine surgeon conflict of interest disclosures between a national meeting and physician payment listings on device manufacturer web sites. Spine J. 2013 Dec;13(12):1780–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

