A Transcription Activator-Like Effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola Activates Rice Gene Os09g29100 to Suppress Rice Immunity
- PMID: 28698641
- PMCID: PMC5505973
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-04800-8
A Transcription Activator-Like Effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola Activates Rice Gene Os09g29100 to Suppress Rice Immunity
Abstract
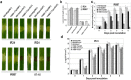
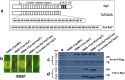
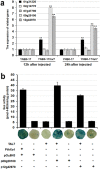
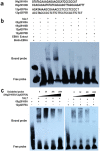
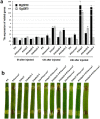
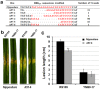
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc) and X. oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) cause bacterial leaf streak (BLS) and bacterial leaf blight (BLB) in rice, respectively. Unlike Xoo, endogenous avirulence-resistance (avr-R) gene interactions have not been identified in the Xoc-rice pathosystem; however, both pathogens possess transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) that are known to modulate R or S genes in rice. The transfer of individual tal genes from Xoc RS105 (hypervirulent) into Xoc YNB0-17 (hypovirulent) led to the identification of tal7, which suppressed avrXa7-Xa7 mediated defense in rice containing an Xa7 R gene. Mobility shift and microscale thermophoresis assays showed that Tal7 bound two EBE sites in the promoters of two rice genes, Os09g29100 and Os12g42970, which encode predicted Cyclin-D4-1 and GATA zinc finger family protein, respectively. Assays using designer TALEs and a TALE-free strain of Xoo revealed that Os09g29100 was the biologically relevant target of Tal7. Tal7 activates the expression of rice gene Os09g29100 that suppresses avrXa7-Xa7 mediated defense in Rice. TALEN editing of the Tal7-binding site in the Os09g29100 gene promoter further enhanced resistance to the pathogen Xoc RS105. The suppression of effector-trigger immunity (ETI) is a phenomenon that may contribute to the scarcity of BLS resistant cultivars.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AvrXa7-Xa7 mediated defense in rice can be suppressed by transcriptional activator-like effectors TAL6 and TAL11a from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014 Sep;27(9):983-95. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-09-13-0279-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014. Retraction in: Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014 Dec;27(12):1413. PMID: 25105804 Retracted.
-
A transcription activator-like effector from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola elicits dose-dependent resistance in rice.Mol Plant Pathol. 2017 Jan;18(1):55-66. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12377. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017. PMID: 26821568 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola effector Tal10a directly activates rice OsHXK5 expression to facilitate pathogenesis.Plant J. 2024 Sep;119(5):2423-2436. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16929. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 38995679
-
TALEs as double-edged swords in plant-pathogen interactions: Progress, challenges, and perspectives.Plant Commun. 2022 May 9;3(3):100318. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100318. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Plant Commun. 2022. PMID: 35576155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Creation of novel alleles of fragrance gene OsBADH2 in rice through CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene editing.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 12;15(8):e0237018. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237018. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32785241 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic Expression of Executor Gene Xa23 Enhances Resistance to Both Bacterial and Fungal Diseases in Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 11;23(12):6545. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126545. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35742990 Free PMC article.
-
SlCNGC1 and SlCNGC14 Suppress Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola-Induced Hypersensitive Response and Non-host Resistance in Tomato.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Mar 6;9:285. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00285. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29559989 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Editing in Rice: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Implications.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Sep 19;9:1361. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01361. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30283477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear effectors of plant pathogens: Distinct strategies to be one step ahead.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Jun;24(6):637-650. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13315. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36942744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fang CT, et al. A comparison of the rice bacterial leaf blight organism with the bacterial leaf streak organism of rice and Leersia hexandra Swartz. Acta Microbiol Sinica. 1957;3:99–124.
-
- Swings J, et al. Reclassification of the causal agents of bacterial blight Xanthomonas campestris pathovar oryzae and bacterial leaf streak Xanthomonas campestris pathovar oryzicola of rice as pathovars of Xanthomonas oryzae new species ex ishiyama 1922. sp. nov, nom. rev. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1990;40:309–311. doi: 10.1099/00207713-40-3-309. - DOI
-
- He WA, et al. Research progress on rice resistance to bacterial leaf streak. J. Plant Genet Resour. 2010;11:116–119.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

