Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TAN1 (tRNA acetyltransferase) in eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B)-mediated translation control and stress response
- PMID: 28677085
- PMCID: PMC5496938
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-0857-8
Role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae TAN1 (tRNA acetyltransferase) in eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B)-mediated translation control and stress response
Abstract
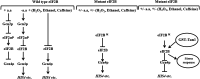
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B) controls the first step of translation by catalyzing guanine nucleotide exchange on eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2). Mutations in the genes encoding eIF2B subunits inhibit the nucleotide exchange and eventually slow down the process of translation, causing vanishing white matter disease. We constructed a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic DNA library in YEp24 vector and screened it for the identification of extragenic suppressors of eIF2B mutations, corresponding to human eIF2B mutations. We found a suppressor-II (Sup-II) genomic clone, as suppressor of eIF2Bβ (gcd7-201) mutation. Identification of Sup-II reveals the presence of truncated SEC15, full-length TAN1 (tRNA acetyltransferase), full-length EMC4, full-length YGL230C (putative protein) and truncated SAP4 genes. Full-length TAN1 (tRNA acetyltransferase) gene, subcloned into pEG(KG) vector and overexpressed in gcd7-201 gcn2∆ strain, suppresses the slow-growth (Slg-) and general control derepression (Gcd-) phenotype of gcd7-201 gcn2∆ mutation, but YGL230C did not show any effect. A GST-Tan1p fusion protein of 60 kDa was detected by western blotting using α-GST antibodies. Interestingly, Tan1p overexpression also suppresses the temperature-sensitive (Ts-), Slg- and Gcd- phenotype of eIF2Bγ (gcd1-502) mutant. Role of Tan1p protein in eIF2B-mediated translation regulation was also studied. Results revealed that Tan1p overexpression confers resistance to GCD7 GCN2, gcd7-201 gcn2∆, GCD7 gcn2∆ growth defect under ethanol, H2O2 and caffeine stress. No resistance to DMSO-, NaCl- and DTT-mediated growth defect upon GCD7 gcn2∆, GCD7 GCN2, gcd7-201 gcn2∆ was observed by overexpression of TAN1. Hence, we proposed that Tan1p is involved directly or indirectly in regulating eIF2B-mediated translation.
Keywords: Caffeine; Ethanol; H2O2; Tan1 p; Translation; VWM; eIF2B.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding and support
Shoolini University.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae ER membrane protein complex subunit 4 (EMC4) plays a crucial role in eIF2B-mediated translation regulation and survival under stress conditions.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 1;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s43141-020-00029-7. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32476094 Free PMC article.
-
The beta/Gcd7 subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (eIF2B), a guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is crucial for binding eIF2 in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;30(21):5218-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00265-10. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20805354 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a regulatory subcomplex in the guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B that mediates inhibition by phosphorylated eIF2.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Nov;16(11):6603-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.11.6603. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8887689 Free PMC article.
-
[Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B and leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Oct 18;41(5):608-10. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19829687 Review. Chinese.
-
Localization of the translational guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B: a common theme for GEFs?Cell Cycle. 2006 Apr;5(7):678-80. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.7.2607. Epub 2006 Apr 1. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16582624 Review.
Cited by
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae ER membrane protein complex subunit 4 (EMC4) plays a crucial role in eIF2B-mediated translation regulation and survival under stress conditions.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 1;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s43141-020-00029-7. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32476094 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

