A Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS) assay for profiling human norovirus antibodies
- PMID: 28673856
- PMCID: PMC5592151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.06.017
A Luciferase Immunoprecipitation System (LIPS) assay for profiling human norovirus antibodies
Abstract
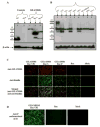
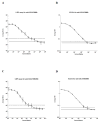
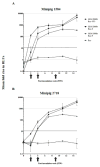
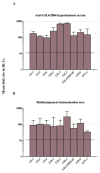
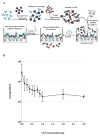
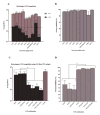
A luciferase immunoprecipitation systems (LIPS) assay was developed to define the antigenic specificity and titer of antibodies directed against human norovirus (HuNoV). Recombinant proteins, expressed by plasmid constructs encoding Renilla luciferase (Ruc) fused to the full-length HuNoV major capsid protein (VP1) (Ruc-antigen), were generated for ten HuNoV strains. In addition, subdomain constructs Ruc-Shell (S) and Ruc-Protruding (P) were engineered for a representative GII.4 norovirus (strain GII.4/2006b). The LIPS assay measured antibody levels in a well-defined panel of HuNoV-specific sera, and the results were compared to an ELISA standard. In hyperimmune sera, the LIPS produced titers similar to or higher than those measured by the ELISA of HuNoV-specific antibodies. The specificity of antibodies in various sera was profiled by LIPS with a panel of diverse Ruc-antigens containing full-length HuNoV VP1 proteins or VP1 subdomains, and the assay detected both specific and cross-reactive antibodies. Competition assays, in which antibodies were pre-incubated with one or more intact VLPs representing different genotypes, proved useful in further assessment of the antibody specificity detected by LIPS in complex polyclonal sera. The profiling of HuNoV-specific antibodies in the high-throughput LIPS format may prove useful in defining the strength or specificity of the adaptive immune response following natural infection or vaccination.
Keywords: ELISA; Human norovirus; LIPS assay; Serum antibody.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type-specific and cross-reactive antibodies and T cell responses in norovirus VLP immunized mice are targeted both to conserved and variable domains of capsid VP1 protein.Mol Immunol. 2016 Oct;78:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27573255
-
Functionality and avidity of norovirus-specific antibodies and T cells induced by GII.4 virus-like particles alone or co-administered with different genotypes.Vaccine. 2018 Jan 25;36(4):484-490. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Vaccine. 2018. PMID: 29246474
-
Norovirus GII.17 Virus-Like Particles Bind to Different Histo-Blood Group Antigens and Cross-React with Genogroup II-Specific Mouse Sera.Viral Immunol. 2018 Dec;31(10):649-657. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0115. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Viral Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30431404
-
The Antigenic Topology of Norovirus as Defined by B and T Cell Epitope Mapping: Implications for Universal Vaccines and Therapeutics.Viruses. 2019 May 10;11(5):432. doi: 10.3390/v11050432. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31083353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape.Viruses. 2019 Feb 20;11(2):177. doi: 10.3390/v11020177. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30791623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A luciferase-based approach for measuring HBGA blockade antibody titers against human norovirus.J Virol Methods. 2021 Nov;297:114196. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114196. Epub 2021 May 19. J Virol Methods. 2021. PMID: 34019938 Free PMC article.
-
Coelenterazine-Dependent Luciferases as a Powerful Analytical Tool for Research and Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 10;21(20):7465. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207465. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring Silent Spillovers Before Emergence: A Pilot Study at the Tick/Human Interface in Thailand.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 17;10:2315. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02315. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31681195 Free PMC article.
-
THSD7A as a Promising Biomarker for Membranous Nephrosis.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;66(11):3117-3135. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00934-5. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37884765 Review.
-
Preparation of Luciferase-fused Peptides for Immunoassay of Amyloid Beta.Anal Sci. 2021 May 10;37(5):759-763. doi: 10.2116/analsci.20SCP19. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Anal Sci. 2021. PMID: 33583860
References
-
- Atmar RL, Bernstein DI, Lyon GM, Treanor JJ, Al-Ibrahim MS, Graham DY, Vinje J, Jiang X, Gregoricus N, Frenck RW, Moe CL, Chen WH, Ferreira J, Barrett J, Opekun AR, Estes MK, Borkowski A, Baehner F, Goodwin R, Edmonds A, Mendelman PM. Serological correlates of protection against a GII.4 norovirus. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015;22:923–9. doi: 10.1128/cvi.00196-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belliot G, Noel JS, Li JF, Seto Y, Humphrey CD, Ando T, Glass RI, Monroe SS. Characterization of capsid genes, expressed in the baculovirus system, of three new genetically distinct strains of Norwalk-like viruses. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:4288–95. doi: 10.1128/jcm.39.12.4288-4295.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

