The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Channel 6 Channels in the Pulmonary Vasculature
- PMID: 28670316
- PMCID: PMC5472666
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00707
The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Channel 6 Channels in the Pulmonary Vasculature
Abstract
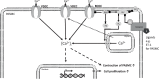
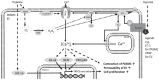
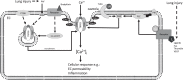
Canonical or classical transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) is a Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channel that is widely expressed in the heart, lung, and vascular tissues. The use of TRPC6-deficient ("knockout") mice has provided important insights into the role of TRPC6 in normal physiology and disease states of the pulmonary vasculature. Evidence indicates that TRPC6 is a key regulator of acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Moreover, several studies implicated TRPC6 in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension. Furthermore, a unique genetic variation in the TRPC6 gene promoter has been identified, which might link the inflammatory response to the upregulation of TRPC6 expression and ultimate development of pulmonary vascular abnormalities in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Additionally, TRPC6 is critically involved in the regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability and lung edema formation during endotoxin or ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury. In this review, we will summarize latest findings on the role of TRPC6 in the pulmonary vasculature.
Keywords: hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction; pulmonary hypertension; transient receptor potential channel 6; transient receptor potential channels; vascular permeability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Classical transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) is essential for hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and alveolar gas exchange.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 12;103(50):19093-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606728103. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17142322 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Activation of Ca(2+) Signaling in the Development of Hypoxic Pulmonary Vasoconstriction and Pulmonary Hypertension.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Sep;53(3):355-67. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0235OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25569851 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced expression of transient receptor potential channels in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Sep 21;101(38):13861-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405908101. Epub 2004 Sep 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15358862 Free PMC article.
-
The role of classical transient receptor potential channels in the regulation of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;661:187-200. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20204731 Review.
-
TRPC6.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(179):125-41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34891-7_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17217054 Review.
Cited by
-
TRPC6 regulates phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells through plasma membrane potential-dependent coupling with PTEN.FASEB J. 2019 Sep;33(9):9785-9796. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802811R. Epub 2019 Jun 4. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 31162976 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow-Derived Endothelial Progenitor Cells Contribute to Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Rats via Inhibition of Store-Operated Ca2+ Channels.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 18;2018:4892349. doi: 10.1155/2018/4892349. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30320134 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of vascular tone homeostasis by NO and H2S: Implications in hypertension.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;149:42-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.017. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29330066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) Channels: Then and Now.Cells. 2020 Aug 28;9(9):1983. doi: 10.3390/cells9091983. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32872338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB/p65 Competes With Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma for Transient Receptor Potential Channel 6 in Hypoxia-Induced Human Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 7;9:656625. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.656625. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34950652 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

