Inhibition of HDAC6 activity through interaction with RanBPM and its associated CTLH complex
- PMID: 28668087
- PMCID: PMC5494137
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3430-2
Inhibition of HDAC6 activity through interaction with RanBPM and its associated CTLH complex
Abstract
Background: Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) is a microtubule-associated deacetylase that promotes many cellular processes that lead to cell transformation and tumour development. We previously documented an interaction between Ran-Binding Protein M (RanBPM) and HDAC6 and found that RanBPM expression inhibits HDAC6 activity. RanBPM is part of a putative E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, termed the C-terminal to LisH (CTLH) complex. Here, we investigated the involvement of the CTLH complex on HDAC6 inhibition and assessed the outcome of this regulation on the cellular motility induced by HDAC6.
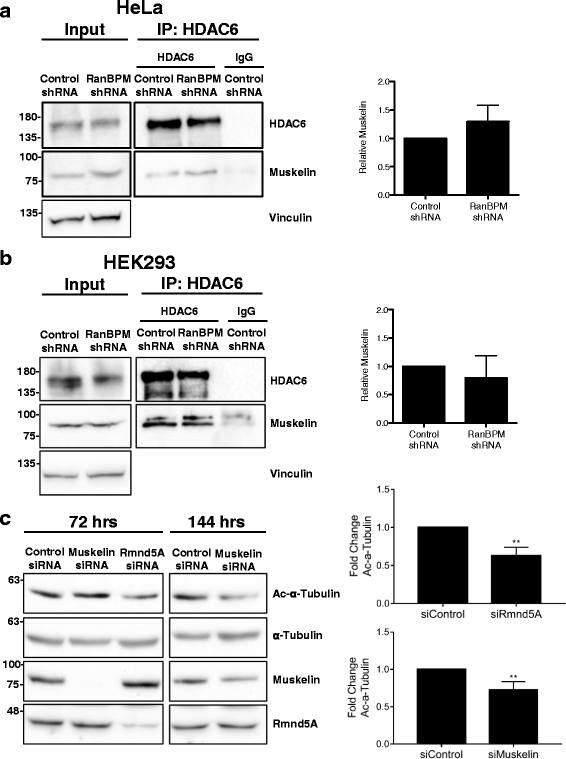
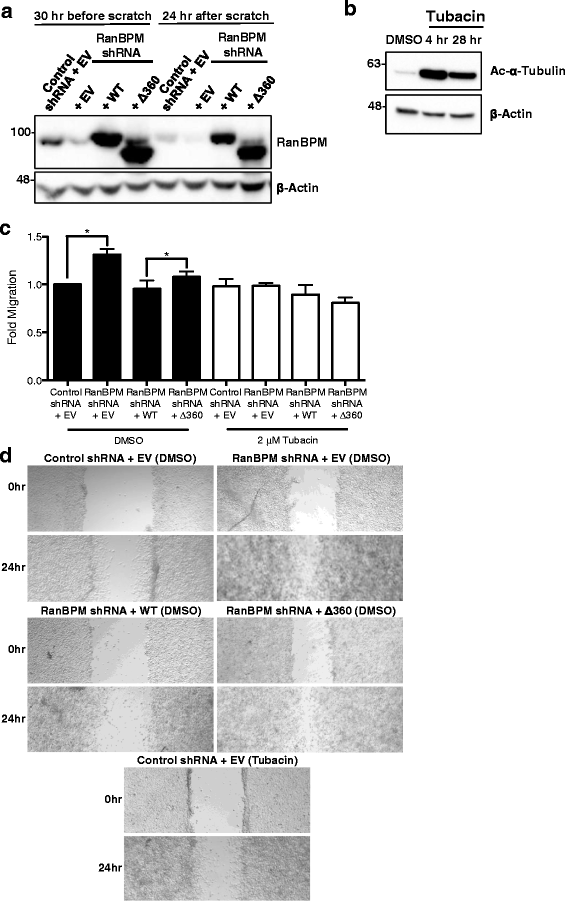
Methods: Cell lines (Hela, HEK293 and immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts) stably or transiently downregulated for several components of the CTLH complex were employed for the assays used in this study. Interactions of HDAC6, RanBPM and muskelin were assessed by co-immunoprecipitations. Quantifications of western blot analyses were employed to evaluate acetylated α-tubulin levels. Confocal microscopy analyses were used to determine microtubule association of HDAC6 and CTLH complex members. Cell migration was evaluated using wound healing assays.
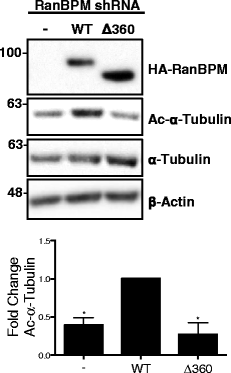
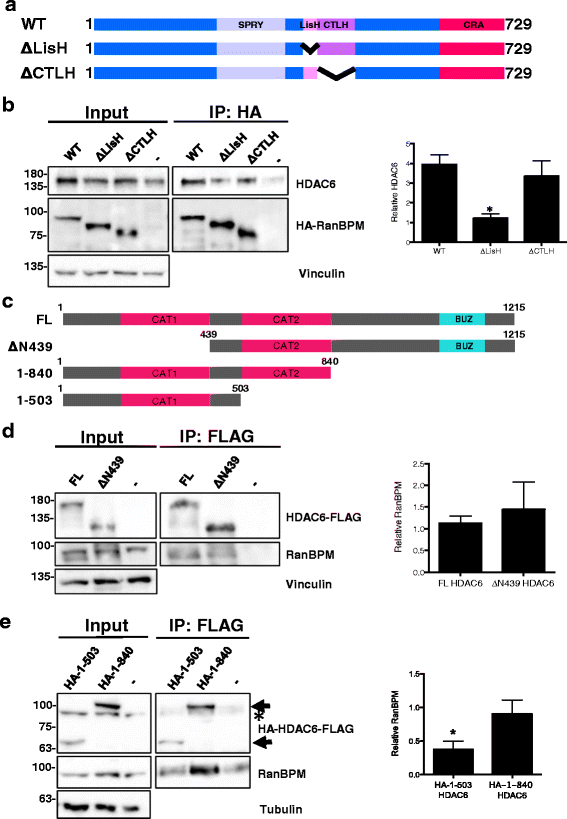
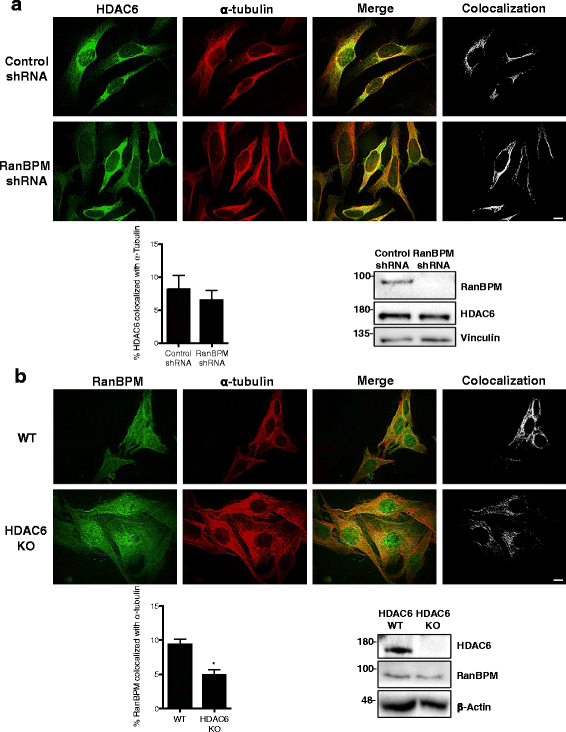
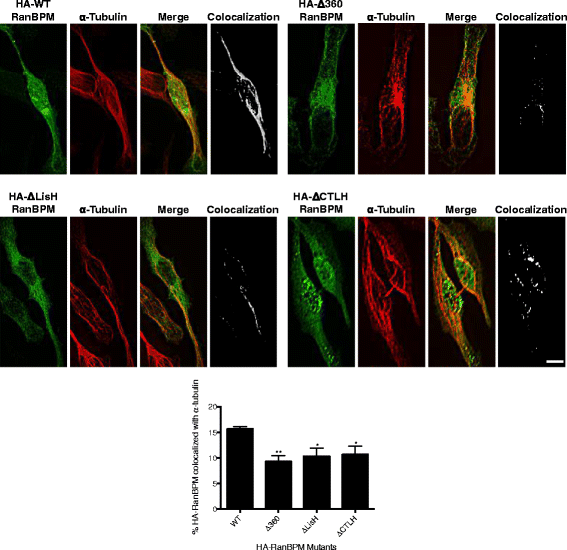
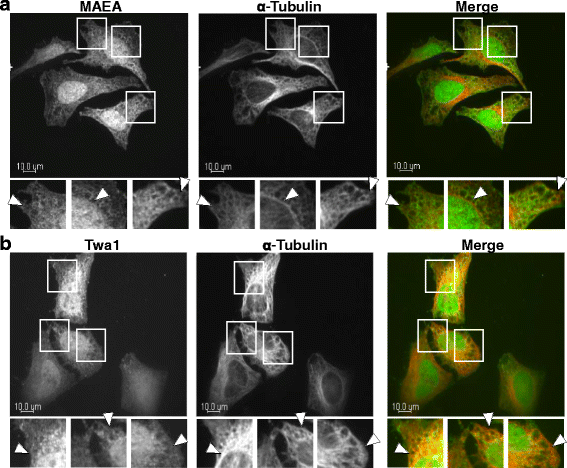
Results: We demonstrate that RanBPM-mediated inhibition of HDAC6 is dependent on its association with HDAC6. We show that, while HDAC6 does not require RanBPM to associate with microtubules, RanBPM association with microtubules requires HDAC6. Additionally, we show that Twa1 (Two-hybrid-associated protein 1 with RanBPM) and MAEA (Macrophage Erythroblast Attacher), two CTLH complex members, also associate with α-tubulin and that muskelin, another component of the CTLH complex, is able to associate with HDAC6. Downregulation of CTLH complex members muskelin and Rmnd5A (Required for meiotic nuclear division homolog A) resulted in decreased acetylation of HDAC6 substrate α-tubulin. Finally, we demonstrate that the increased cell migration resulting from downregulation of RanBPM is due to the relief in inhibition of HDAC6 α-tubulin deacetylase activity.
Conclusions: Our work shows that RanBPM, together with the CTLH complex, associates with HDAC6 and restricts cell migration through inhibition of HDAC6 activity. This study uncovers a novel function for the CTLH complex and suggests that it could have a tumour suppressive role in restricting HDAC6 oncogenic properties.
Keywords: CTLH complex; Cell migration; HDAC6; RanBPM; α-tubulin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of c-Raf Stability through the CTLH Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 21;20(4):934. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040934. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30795516 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular phylogeny of a RING E3 ubiquitin ligase, conserved in eukaryotic cells and dominated by homologous components, the muskelin/RanBPM/CTLH complex.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e75217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075217. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24143168 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of an Arabidopsis RanBPM homologue with LisH-CTLH domain proteins revealed high conservation of CTLH complexes in eukaryotes.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Jun 7;12:83. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-83. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22676313 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signalling pathway regulation by RanBPM: molecular insights and disease implications.Open Biol. 2017 Jun;7(6):170081. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170081. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28659384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse roles of the scaffolding protein RanBPM.Drug Discov Today. 2012 Apr;17(7-8):379-87. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.030. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Drug Discov Today. 2012. PMID: 22094242 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of c-Raf Stability through the CTLH Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 21;20(4):934. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040934. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30795516 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC6/HNF4α loop mediated by miR-1 promotes bile acids-induced gastric intestinal metaplasia.Gastric Cancer. 2021 Jan;24(1):103-116. doi: 10.1007/s10120-020-01108-x. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Gastric Cancer. 2021. PMID: 32705446 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of ubiquitination substrates reveals a CTLH E3 ligase complex-dependent regulation of glycolysis.FASEB J. 2021 Sep;35(9):e21825. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100664R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 34383978 Free PMC article.
-
Muskelin acts as a substrate receptor of the highly regulated Drosophila CTLH E3 ligase during the maternal-to-zygotic transition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 1:2024.06.28.601265. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.28.601265. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39005399 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Structural and Functional Insights into GID/CTLH E3 Ligase Complexes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 24;23(11):5863. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115863. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kobayashi N, Yang J, Ueda A, Suzuki T, Tomaru K, Takeno M, et al. RanBPM, Muskelin, p48EMLP, p44CTLH, and the armadillo-repeat proteins ARMC8alpha and ARMC8beta are components of the CTLH complex. Gene. 2007;396:236–47. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

