The whole set of the constitutive promoters recognized by four minor sigma subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
- PMID: 28666008
- PMCID: PMC5493296
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179181
The whole set of the constitutive promoters recognized by four minor sigma subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase
Abstract
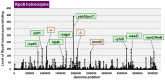
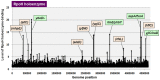
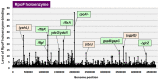
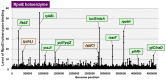
The promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP) is determined by the sigma subunit. The model prokaryote Escherichia coli K-12 contains seven species of the sigma subunit, each recognizing a specific set of promoters. For identification of the "constitutive promoters" that are recognized by each RNAP holoenzyme alone in the absence of other supporting factors, we have performed the genomic SELEX screening in vitro for their binding sites along the E. coli K-12 W3110 genome using each of the reconstituted RNAP holoenzymes and a collection of genome DNA segments of E. coli K-12. The whole set of constitutive promoters for each RNAP holoenzyme was then estimated based on the location of RNAP-binding sites. The first successful screening of the constitutive promoters was achieved for RpoD (σ70), the principal sigma for transcription of growth-related genes. As an extension, we performed in this study the screening of constitutive promoters for four minor sigma subunits, stationary-phase specific RpoS (σ38), heat-shock specific RpoH (σ32), flagellar-chemotaxis specific RpoF (σ28) and extra-cytoplasmic stress-response RpoE (σ24). The total number of constitutive promoters were: 129~179 for RpoS; 101~142 for RpoH; 34~41 for RpoF; and 77~106 for RpoE. The list of constitutive promoters were compared with that of known promoters identified in vivo under various conditions and using varieties of E. coli strains, altogether allowing the estimation of "inducible promoters" in the presence of additional supporting factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole set of constitutive promoters for RpoN sigma factor and the regulatory role of its enhancer protein NtrC in Escherichia coli K-12.Microb Genom. 2021 Nov;7(11):000653. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000653. Microb Genom. 2021. PMID: 34787538 Free PMC article.
-
The whole set of constitutive promoters recognized by RNA polymerase RpoD holoenzyme of Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 6;9(3):e90447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090447. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24603758 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase sigmaF holoenzyme involved in transcription of flagellar and chemotaxis genes.J Bacteriol. 1997 Jul;179(13):4264-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.13.4264-4269.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9209042 Free PMC article.
-
Building a complete image of genome regulation in the model organism Escherichia coli.J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2018 Jan 15;63(6):311-324. doi: 10.2323/jgam.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28904250 Review.
-
The molecular basis of selective promoter activation by the sigmaS subunit of RNA polymerase.Mol Microbiol. 2007 Mar;63(5):1296-306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05601.x. Mol Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17302812 Review.
Cited by
-
σS-Mediated Stress Response Induced by Outer Membrane Perturbation Dampens Virulence in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 30;12:750940. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.750940. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34659184 Free PMC article.
-
Global Regulation by CsrA and Its RNA Antagonists.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Mar;6(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0009-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0009-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 29573256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disentangling direct from indirect relationships in association networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 11;119(2):e2109995119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109995119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 34992138 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-Dependent Influence of FliA Overexpression on PHL628 E. coli Biofilm Growth and Composition.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Dec 17;11:775270. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.775270. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34976858 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription activator AtxA from Bacillus anthracis was employed for developing a tight-control, high-level, modulable and stationary-phase-specific transcription activity in Escherichia coli.Synth Biol (Oxf). 2022 Aug 17;7(1):ysac014. doi: 10.1093/synbio/ysac014. eCollection 2022. Synth Biol (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 36046151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawakami K., Saitoh T. and Ishihama A. (1979) Biosynthesis of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli: Growth-dependent variations in the synthesis rate, content and distribution of RNA polymerase. Mol. Gen. Genet., 174, 107–116. - PubMed
-
- Ishihama A. (1999) Modulation of the nucleoid, the transcription apparatus, and the translation machinery in bacteria for stationary phase survival. Genes Cells, 4, 135–143. - PubMed
-
- Ishihama A. (2000) Functional modulation of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 54, 499–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.499 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishihama A. (2010) Prokaryotic genome regulation: Multi-factor promoters, multi-target regulators and hierarchic networks. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 34, 628–645. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00227.x - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

