SIRT1 and SIRT6 Signaling Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease Protection
- PMID: 28661724
- PMCID: PMC5824538
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7178
SIRT1 and SIRT6 Signaling Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease Protection
Abstract
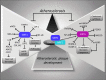
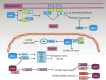
Significance: Oxidative stress represents the common hallmark of pathological conditions associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD), including atherosclerosis, heart failure, hypertension, aging, diabetes, and other vascular system-related diseases. The sirtuin (SIRT) family, comprising seven proteins (SIRT1-SIRT7) sharing a highly conserved nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)-binding catalytic domain, attracted a great attention for the past few years as stress adaptor and epigenetic enzymes involved in the cellular events controlling aging-related disorder, cancer, and CVD. Recent Advances: Among sirtuins, SIRT1 and SIRT6 are the best characterized for their protective roles against inflammation, vascular aging, heart disease, and atherosclerotic plaque development. This latest role has been only recently unveiled for SIRT6. Of interest, in recent years, complex signaling networks controlled by SIRT1 and SIRT6 common to stress resistance, vascular aging, and CVD have emerged.
Critical issues: We provide a comprehensive overview of recent developments on the molecular signaling pathways controlled by SIRT1 and SIRT6, two post-translational modifiers proven to be valuable tools to dampen inflammation and oxidative stress at the cardiovascular level.
Future directions: A deeper understanding of the epigenetic mechanisms through which SIRT1 and SIRT6 act in the signalings responsible for onset and development CVD is a prime scientific endeavor of the upcoming years. Multiple "omic" technologies will have widespread implications in understanding such mechanisms, speeding up the achievement of selective and efficient pharmacological modulation of sirtuins for future applications in the prevention and treatment of CVD. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 711-732.
Keywords: SIRT1; SIRT6; cardiovascular disease; endothelial dysfunction; oxidative stress; vascular aging.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of SIRT6 on cholesterol crystal-induced endothelial dysfunction via regulating ACE2 expression.Exp Cell Res. 2021 May 1;402(1):112526. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112526. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33631165
-
The role of sirtuins in cardiac disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov;309(9):H1375-89. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00053.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26232232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT1 and SIRT6: The role in aging-related diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023 Oct;1869(7):166815. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166815. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023. PMID: 37499928 Review.
-
Sirtuin family in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1186231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186231. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37483618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular biology of sirtuins in cardiovascular disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Aug;164:114931. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114931. Epub 2023 May 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37263163 Review.
Cited by
-
Benefits of Taurisolo in Diabetic Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Jun 4;11(6):174. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11060174. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 38921674 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and obesity-induced endothelial dysfunction: key paradigms in molecular therapy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020 Sep 9;19(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12933-020-01107-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020. PMID: 32907629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of estrogen related receptorα in complications of non-small cell lung cancers.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):258. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12519. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33664821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure.Circ Res. 2021 May 14;128(10):1487-1513. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318241. Epub 2021 May 13. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33983836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress and senescence in aging kidneys: the protective role of SIRT1.EXCLI J. 2024 Aug 27;23:1030-1067. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7519. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 39391060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhmedov A, Camici GG, Reiner MF, Bonetti N, Costantino S, Holy EW, Spescha RD, Stivala S, Schaub Clerigué A, Speer T, Breitenstein A, Manz J, Lohmann C, Paneni F, Beer JH, and Lüscher TF. Endothelial LOX-1 activation differentially regulates arterial thrombus formation depending on oxLDL Levels: role of the Oct-1/SIRT1 and ERK1/2 pathways. Cardiovasc Res 113: 498–507, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Albiero M, Poncina N, Tjwa M, Ciciliot S, Menegazzo L, Ceolotto G, Vigili de Kreutzenberg S, Moura R, Giorgio M, Pelicci P, Avogaro A, and Fadini GP. Diabetes causes bone marrow autonomic neuropathy and impairs stem cell mobilization via dysregulated p66Shc and Sirt1. Diabetes 4: 1353–1365, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Alcendor RR, Gao S, Zhai P, Zablocki D, Holle E, Yu X, Tian B, Wagner T, Vatner SF, and Sadoshima J. Sirt1 regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart. Circ Res 100: 1512–1521, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Alcendor RR, Kirshenbaum LA, Imai S, Vatner SF, and Sadoshima J. Silent information regulator 2alpha, a longevity factor and class III histone deacetylase, is an essential endogenous apoptosis inhibitor incardiac myocytes. Circ Res 95: 971–980, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

