Assessing Free-Radical-Mediated DNA Damage during Cardiac Surgery: 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine as a Putative Biomarker
- PMID: 28660009
- PMCID: PMC5474244
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9715898
Assessing Free-Radical-Mediated DNA Damage during Cardiac Surgery: 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine as a Putative Biomarker
Abstract
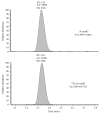
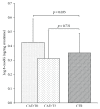
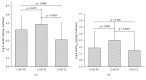
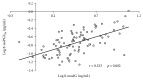
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), one of the most common cardiac surgical procedures, is characterized by a burst of oxidative stress. 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodG), produced following DNA repairing, is used as an indicator of oxidative DNA damage in humans. The effect of CABG on oxidative-induced DNA damage, evaluated through the measurement of urinary 8-oxodG by a developed and validated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method in 52 coronary artery disease (CAD) patients, was assessed before (T0), five days (T1), and six months (T2) after CABG procedure. These results were compared with those obtained in 40 subjects with cardiovascular risk factors and without overt cardiovascular disease (CTR). Baseline (T0) 8-oxodG was higher in CAD than in CTR (p = 0.035). A significant burst was detected at T1 (p = 0.019), while at T2, 8-oxodG levels were significantly lower than those measured at T0 (p < 0.0001) and comparable to those found in CTR (p = 0.73). A similar trend was observed for urinary 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (8-isoPGF2α ), a reliable marker of oxidative stress. In the whole population baseline, 8-oxodG significantly correlated with 8-isoPGF2α levels (r = 0.323, p = 0.002). These data argue for CABG procedure in CAD patients as inducing a short-term increase in oxidative DNA damage, as revealed by 8-oxodG concentrations, and a long-term return of such metabolite toward physiological levels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of 8-oxo-2'-deoxyguanosine and 8-oxo-2'-deoxyadenosine in DNA using online column-switching liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009 Jan;23(1):151-60. doi: 10.1002/rcm.3866. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2009. PMID: 19065576
-
Urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine analysis by an improved ELISA: An inter-laboratory comparison study.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Jun;95:169-79. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.03.016. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27016072
-
Low 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine levels and influence of genetic background in an Andean population exposed to high levels of arsenic.Mutat Res. 2010 Jan 5;683(1-2):98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.10.014. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 19896490
-
8-hydroxy-2' -deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis.J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2009 Apr;27(2):120-39. doi: 10.1080/10590500902885684. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19412858 Review.
-
[Free radical oxidation of DNA and its biomarker oxidized guanosine(8-oxodG)].Vopr Med Khim. 2002 Sep-Oct;48(5):419-31. Vopr Med Khim. 2002. PMID: 12498082 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
GSTM2 alleviates heart failure by inhibiting DNA damage in cardiomyocytes.Cell Biosci. 2023 Nov 30;13(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01168-3. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38037116 Free PMC article.
-
8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine and 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α: Putative Biomarkers to assess Oxidative Stress Damage Following Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP).J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 17;11(20):6102. doi: 10.3390/jcm11206102. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294423 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Scavengers, Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Disease.J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 6;8(11):1895. doi: 10.3390/jcm8111895. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31698880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerritsen W. B., Aarts L. P., Morshuis W. J., Haas F. J. Indices of oxidative stress in urine of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. European Journal of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry. 1997;35(10):737–742. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

