MicroRNA-433-3p promotes osteoblast differentiation through targeting DKK1 expression
- PMID: 28628652
- PMCID: PMC5476290
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179860
MicroRNA-433-3p promotes osteoblast differentiation through targeting DKK1 expression
Abstract
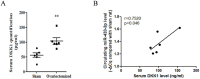
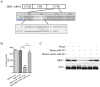
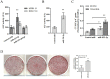
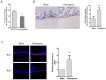
Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) is a powerful antagonist of canonical WNT signaling pathway, and is regarded as a biomarker for osteoporosis. Its expression is highly correlated with bone mass and osteoblasts maturation. In this study, mouse primary bone marrow cells and osteoblast cell lines were used. Luciferase reporter assay and western blotting methods were employed to validate if miRNA-433-3p epigenetically regulated DKK1 translation. Rat bone marrow derived osteoblasts were infected with lentivirus vector in which miR-433-3p was constructed. The authors constructed lentivirus mediated miRNA-433-3p stable expression and examined the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and mineral deposition level in vitro. In situ hybridization method was used to observe miR-433-3p in primary osteoblasts. We built up an OVX rat model to mimic postmenopausal osteoporosis, and found aberrant circulating miR-433-3p and miR-106b, which were not reported previously. Results showed that miR-433-3p potentially regulated DKK1 mRNA, Furthermore, the correlation of serum DKK1 with circulating miR-433-3p level was significant (r = 0.7520, p = 0.046). In the luciferase reporter assay, we found that miR-433-3p siRNA decreased luminescence signal, indicating direct regulation of miR-433-3p on DKK1 mRNA. When the miR-433-3p binding site in DKK1 3'UTR was mutant, such reduction was prohibited. Western blotting result validated that miR-433-3p inhibited over 90% of DKK1 protein expression. Similarly, the change of protein expression was not observed in mutant group. The stable expression of lentivirus mediated miR-433-3p increased ALP activity and mineralization both in human and rat derived immortalized cells. We found that primary osteoblasts had higher miR-433-3p level compared with immortal cells through real-time PCR, as well as in situ hybridization experiment. Conclusively, our findings further emphasized the vital role of miR-433-3p in DKK1/WNT/β-catenin pathway through decreasing DKK1 expression and inducing osteoblasts differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dkk1-induced inhibition of Wnt signaling in osteoblast differentiation is an underlying mechanism of bone loss in multiple myeloma.Bone. 2008 Apr;42(4):669-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.12.006. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Bone. 2008. PMID: 18294945
-
MiR-214 inhibits human mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into osteoblasts through targeting β-catenin.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Nov;21(21):4777-4783. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29164587
-
MiR-9 promotes osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting DKK1 gene expression.Mol Biol Rep. 2016 Sep;43(9):939-46. doi: 10.1007/s11033-016-4030-y. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27393149
-
Perspectives on miRNAs Targeting DKK1 for Developing Hair Regeneration Therapy.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2957. doi: 10.3390/cells10112957. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dickkopf-1: A Promising Target for Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 20;12:658097. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658097. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Signaling Pathways and MicroRNAs in Bone Remodeling: A Narrative Review.Diseases. 2024 Oct 12;12(10):252. doi: 10.3390/diseases12100252. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 39452495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of bone homeostasis: signaling pathways and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 24;5(8):e657. doi: 10.1002/mco2.657. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39049966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling Mesenchymal Stem Cells' Regenerative Potential in Clinical Applications: Insights in miRNA and lncRNA Implications.Cells. 2023 Oct 31;12(21):2559. doi: 10.3390/cells12212559. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37947637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of miR-433-3p in vascular calcification in type 2 diabetic patients: targeting WNT/β-Catenin and RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling pathways.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Nov;50(11):9073-9083. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08792-9. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37728820 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating and extracellular vesicle-derived microRNAs as biomarkers in bone-related diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 24;14:1168898. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1168898. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37293498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang W, Drake MT. Potential role for therapies targeting DKK1, LRP5, and serotonin in the treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep, 2012; 10(1): 93–100. doi: 10.1007/s11914-011-0086-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- David R, Brenner C, Stieber J, Schwarz F, Brunner S, Vollmer M, et al. MesP1 drives vertebrate cardiovascular differentiation through Dkk-1-mediated blockade of Wnt-signalling. NAT CELL BIOL, 2008; 10(3): 338–45. doi: 10.1038/ncb1696 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li J, Sarosi I, Cattley RC, Pretorius J, Asuncion F, Grisanti M, et al. Dkk1-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling in bone results in osteopenia. BONE, 2006; 39(4): 754–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.03.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morvan F, Boulukos K, Clement-Lacroix P, Roman RS, Suc-Royer I, Vayssiere B, et al. Deletion of a single allele of the Dkk1 gene leads to an increase in bone formation and bone mass. J BONE MINER RES, 2006; 21(6): 934–45. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.060311 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Florio M, Gunasekaran K, Stolina M, Li X, Liu L, Tipton B, et al. A bispecific antibody targeting sclerostin and DKK-1 promotes bone mass accrual and fracture repair. NAT COMMUN, 2016; 7: 11505 doi: 10.1038/ncomms11505 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

