Identification, Characterization, and Functional Validation of Drought-responsive MicroRNAs in Subtropical Maize Inbreds
- PMID: 28626466
- PMCID: PMC5454542
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00941
Identification, Characterization, and Functional Validation of Drought-responsive MicroRNAs in Subtropical Maize Inbreds
Abstract
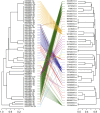
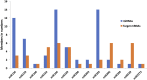
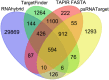
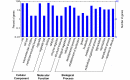
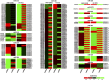
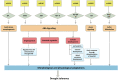
MicroRNA-mediated gene regulation plays a crucial role in controlling drought tolerance. In the present investigation, 13 drought-associated miRNA families consisting of 65 members and regulating 42 unique target mRNAs were identified from drought-associated microarray expression data in maize and were subjected to structural and functional characterization. The largest number of members (14) was found in the zma-miR166 and zma-miR395 families, with several targets. However, zma-miR160, zma-miR390, zma-miR393, and zma-miR2275 each showed a single target. Twenty-three major drought-responsive cis-regulatory elements were found in the upstream regions of miRNAs. Many drought-related transcription factors, such as GAMYB, HD-Zip III, and NAC, were associated with the target mRNAs. Furthermore, two contrasting subtropical maize genotypes (tolerant: HKI-1532 and sensitive: V-372) were used to understand the miRNA-assisted regulation of target mRNA under drought stress. Approximately 35 and 31% of miRNAs were up-regulated in HKI-1532 and V-372, respectively. The up-regulation of target mRNAs was as high as 14.2% in HKI-1532 but was only 2.38% in V-372. The expression patterns of miRNA-target mRNA pairs were classified into four different types: Type I- up-regulation, Type II- down-regulation, Type III- neutral regulation, and Type IV- opposite regulation. HKI-1532 displayed 46 Type I, 13 Type II, and 23 Type III patterns, whereas V-372 had mostly Type IV interactions (151). A low level of negative regulations of miRNA associated with a higher level of mRNA activity in the tolerant genotype helped to maintain crucial biological functions such as ABA signaling, the auxin response pathway, the light-responsive pathway and endosperm expression under stress conditions, thereby leading to drought tolerance. Our study identified candidate miRNAs and mRNAs operating in important pathways under drought stress conditions, and these candidates will be useful in the development of drought-tolerant maize hybrids.
Keywords: drought; gene expression; mRNA; maize; miRNA; post-transcriptional changes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characteristics of microRNAs and Target Genes in Maize Root under Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4968. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094968. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563360 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Novel Maize Mirnas Involved in Different Genetic Background.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 May 22;11(7):781-93. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.11619. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26078720 Free PMC article.
-
Submergence-responsive MicroRNAs are potentially involved in the regulation of morphological and metabolic adaptations in maize root cells.Ann Bot. 2008 Oct;102(4):509-19. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn129. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Ann Bot. 2008. PMID: 18669574 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA (miRNA) profiling of maize genotypes with differential response to Aspergillus flavus implies zma-miR156-squamosa promoter binding protein (SBP) and zma-miR398/zma-miR394-F -box combinations involved in resistance mechanisms.Stress Biol. 2024 May 10;4(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s44154-024-00158-w. Stress Biol. 2024. PMID: 38727957 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of microRNAs in the mediation of drought stress response in plants.J Exp Bot. 2013 Aug;64(11):3077-86. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert164. Epub 2013 Jun 28. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23814278 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs and transposable elements in plant genomes: emergence, regulatory mechanisms and roles in plant development and stress responses.Planta. 2019 Jul;250(1):23-40. doi: 10.1007/s00425-019-03166-7. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Planta. 2019. PMID: 30993403 Review.
-
Plant Non-Coding RNAs: Origin, Biogenesis, Mode of Action and Their Roles in Abiotic Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 9;21(21):8401. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218401. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of Eceriferum (CER) Gene Family in Passion Fruit (Passiflora edulis) Under Fusarium kyushuense and Drought Stress Conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 27;13:898307. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.898307. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35832215 Free PMC article.
-
The Homeodomain-Leucine Zipper Genes Family Regulates the Jinggangmycin Mediated Immune Response of Oryza sativa to Nilaparvata lugens, and Laodelphax striatellus.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;9(8):398. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9080398. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004924 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Comprehensive Identification and In Silico Characterization of Lectin Receptor-Like Kinase Gene Family in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).Genet Res (Camb). 2024 Feb 27;2024:2924953. doi: 10.1155/2024/2924953. eCollection 2024. Genet Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38444770 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

