1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 -induced dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by increasing proportions of the regulatory lymphocytes and reducing T helper type 1 and type 17 cells
- PMID: 28617989
- PMCID: PMC5629429
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12776
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 -induced dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by increasing proportions of the regulatory lymphocytes and reducing T helper type 1 and type 17 cells
Abstract
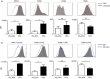
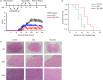
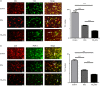
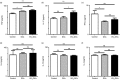
Dendritic cells (DCs), a bridge for innate and adaptive immune responses, play a key role in the development of multiple sclerosis (MS) and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model for MS. Administration of tolerogenic DCs has been used as an immunotherapy in autoimmune diseases. Deficiency of vitamin D is an environmental risk factor of MS. In this study, we induced tolerogenic DCs by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and transferred the tolerogenic DCs (VD3 -DCs) into EAE mice by adoptive transfer. We found that VD3 -DCs inhibited the infiltrations of T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells into spinal cord and increased the proportions of regulatory T cells (CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ ), CD4+ IL-10+ T cells and regulatory B cells (CD19+ CD5+ CD1d+ ) in peripheral immune organs, which resulted in attenuated EAE. However, the proportions of T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th17 cells in spleen and lymph nodes and the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and IgG in serum also increased after transfer of VD3 -DCs. We conclude that transfer of VD3 -DCs suppressed EAE by increasing proportions of regulatory T cells, CD4+ IL-10+ T cells and regulatory B cells in spleen and reducing infiltration of Th1 and Th17 cells into spinal cord, which suggests a possible immunotherapy method using VD3 -DCs in MS.
Keywords: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; multiple sclerosis; tolerogenic dendritic cells.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin controls experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by altering the T effector/regulatory balance.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Nov;50:101-114. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 26130320
-
Inhibition of Interferon Regulatory Factor 4 Suppresses Th1 and Th17 Cell Differentiation and Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.Scand J Immunol. 2015 Oct;82(4):345-51. doi: 10.1111/sji.12334. Scand J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26110284
-
Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Generated with Tofacitinib Ameliorate Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through Modulation of Th17/Treg Balance.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:5021537. doi: 10.1155/2016/5021537. Epub 2016 Dec 13. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 28070525 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting DCs for Tolerance Induction: Don't Lose Sight of the Neutrophils.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 5;12:732992. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732992. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34675923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells induced by vitamin D receptor ligands enhance regulatory T cells inhibiting autoimmune diabetes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;987:258-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb06057.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12727648 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D in Systemic Sclerosis: A Review.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 21;14(19):3908. doi: 10.3390/nu14193908. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36235561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Under the influence: environmental factors as modulators of neuroinflammation through the IL-10/IL-10R axis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 3;14:1188750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188750. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paving the way towards an effective treatment for multiple sclerosis: advances in cell therapy.Cell Mol Immunol. 2021 Jun;18(6):1353-1374. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00618-z. Epub 2021 May 6. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33958746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D in Multiple Sclerosis-Lessons From Animal Studies.Front Neurol. 2021 Oct 20;12:757795. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.757795. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34744990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What are the characteristics of vitamin D metabolism in opioid dependence? An exploratory longitudinal study in Australian primary care.BMJ Open. 2018 Jan 13;8(1):e016806. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016806. BMJ Open. 2018. PMID: 29331964 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hewer S, Lucas R, van der Mei I, Taylor BV. Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis. J Clin Neurosci 2013; 20:634–41. - PubMed
-
- Grigoriadis N, van Pesch V. A basic overview of multiple sclerosis immunopathology. Eur J Neurol 2015; 22(Suppl 2):3–13. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM, Banchereau J. Taking dendritic cells into medicine. Nature 2007; 449:419–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

