N6-methyladenosine is required for the hypoxic stabilization of specific mRNAs
- PMID: 28611253
- PMCID: PMC5558913
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.061044.117
N6-methyladenosine is required for the hypoxic stabilization of specific mRNAs
Abstract
Post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA during oxygen deprivation, or hypoxia, can affect the survivability of cells. Hypoxia has been shown to increase stability of a subset of ischemia-related mRNAs, including VEGF. RNA binding proteins and miRNAs have been identified as important for post-transcriptional regulation of individual mRNAs, but corresponding mechanisms that regulate global stability are not well understood. Recently, mRNA modification by N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has been shown to be involved in post-transcriptional regulation processes including mRNA stability and promotion of translation, but the role of m6A in the hypoxia response is unknown. In this study, we investigate the effect of hypoxia on RNA modifications including m6A. Our results show hypoxia increases m6A content of poly(A)+ messenger RNA (mRNA), but not in total or ribosomal RNA in HEK293T cells. Using m6A mRNA immunoprecipitation, we identify specific hypoxia-modified mRNAs, including glucose transporter 1 (Glut1) and c-Myc, which show increased m6A levels under hypoxic conditions. Many of these mRNAs also exhibit increased stability, which was blocked by knockdown of m6A-specific methyltransferases METTL3/14. However, the increase in mRNA stability did not correlate with a change in translational efficiency or the steady-state amount of their proteins. Knockdown of METTL3/14 did reveal that m6A is involved in recovery of translational efficiency after hypoxic stress. Therefore, our results suggest that an increase in m6A mRNA during hypoxic exposure leads to post-transcriptional stabilization of specific mRNAs and contributes to the recovery of translational efficiency after hypoxic stress.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; hypoxia; mRNA stabilization; methyltransferase; post-transcriptional regulation.
© 2017 Fry et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
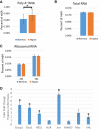
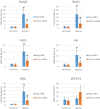
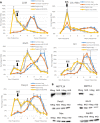
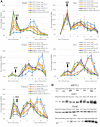
Similar articles
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation.Genes Dev. 2015 Jul 1;29(13):1343-55. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26159994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of METTL3-Dependent N6-Methyladenosine mRNA Modification in the Promotion of Angiogenesis.Mol Ther. 2020 Oct 7;28(10):2191-2202. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.07.022. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Mol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32755566 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic stabilization of mRNA is HIF-independent but requires mtROS.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Oct 4;23:48. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0112-2. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30305827 Free PMC article.
-
RNA m6 A methylation regulates sorafenib resistance in liver cancer through FOXO3-mediated autophagy.EMBO J. 2020 Jun 17;39(12):e103181. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019103181. Epub 2020 May 5. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32368828 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jan;18(1):31-42. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.132. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27808276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A-mRNA Methylation Regulates Gene Expression and Programmable m6A Modification of Cellular RNAs With CRISPR-Cas13b in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jan 21;12:795611. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.795611. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35126463 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the gut microbiota on the m6A epitranscriptome of mouse cecum and liver.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 12;11(1):1344. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15126-x. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32165618 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine modification and the YTHDF2 reader protein play cell type specific roles in lytic viral gene expression during Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Apr 16;14(4):e1006995. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006995. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29659627 Free PMC article.
-
Muscleblind-like 2 controls the hypoxia response of cancer cells.RNA. 2020 May;26(5):648-663. doi: 10.1261/rna.073353.119. Epub 2020 Mar 3. RNA. 2020. PMID: 32127384 Free PMC article.
-
Lumbrokinase (LK) ameliorates diabetic kidney disease renal fibrosis through regulating snail via m6A RNA methyltransferase 3.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 19;14(1):28671. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80168-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562622 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
