Kv2.1 Clustering Contributes to Insulin Exocytosis and Rescues Human β-Cell Dysfunction
- PMID: 28607108
- PMCID: PMC5482075
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-1170
Kv2.1 Clustering Contributes to Insulin Exocytosis and Rescues Human β-Cell Dysfunction
Abstract
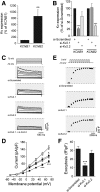
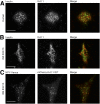
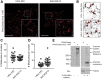
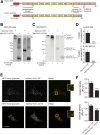
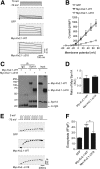
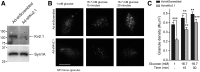
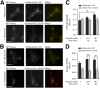
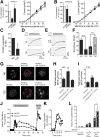
Insulin exocytosis is regulated by ion channels that control excitability and Ca2+ influx. Channels also play an increasingly appreciated role in microdomain structure. In this study, we examine the mechanism by which the voltage-dependent K+ (Kv) channel Kv2.1 (KCNB1) facilitates depolarization-induced exocytosis in INS 832/13 cells and β-cells from human donors with and without type 2 diabetes (T2D). We find that Kv2.1, but not Kv2.2 (KCNB2), forms clusters of 6-12 tetrameric channels at the plasma membrane and facilitates insulin exocytosis. Knockdown of Kv2.1 expression reduces secretory granule targeting to the plasma membrane. Expression of the full-length channel (Kv2.1-wild-type) supports the glucose-dependent recruitment of secretory granules. However, a truncated channel (Kv2.1-ΔC318) that retains electrical function and syntaxin 1A binding, but lacks the ability to form clusters, does not enhance granule recruitment or exocytosis. Expression of KCNB1 appears reduced in T2D islets, and further knockdown of KCNB1 does not inhibit Kv current in T2D β-cells. Upregulation of Kv2.1-wild-type, but not Kv2.1-ΔC318, rescues the exocytotic phenotype in T2D β-cells and increases insulin secretion from T2D islets. Thus, the ability of Kv2.1 to directly facilitate insulin exocytosis depends on channel clustering. Loss of this structural role for the channel might contribute to impaired insulin secretion in diabetes.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kv2.1 clusters on β-cell plasma membrane act as reservoirs that replenish pools of newcomer insulin granule through their interaction with syntaxin-3.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 4;293(18):6893-6904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002703. Epub 2018 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29549124 Free PMC article.
-
The voltage-dependent potassium channel subunit Kv2.1 regulates insulin secretion from rodent and human islets independently of its electrical function.Diabetologia. 2012 Jun;55(6):1709-20. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2512-6. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22411134
-
A glucose-dependent spatial patterning of exocytosis in human β-cells is disrupted in type 2 diabetes.JCI Insight. 2019 May 14;5(12):e127896. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.127896. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31085831 Free PMC article.
-
SNAREing voltage-gated K+ and ATP-sensitive K+ channels: tuning beta-cell excitability with syntaxin-1A and other exocytotic proteins.Endocr Rev. 2007 Oct;28(6):653-63. doi: 10.1210/er.2007-0010. Epub 2007 Sep 18. Endocr Rev. 2007. PMID: 17878408 Review.
-
Insulin granule biogenesis and exocytosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(5):1957-1970. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03688-4. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33146746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activity-dependent endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ uptake depends on Kv2.1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum/plasma membrane junctions to promote synaptic transmission.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 26;119(30):e2117135119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2117135119. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35862456 Free PMC article.
-
Beta cell identity changes with mild hyperglycemia: Implications for function, growth, and vulnerability.Mol Metab. 2020 May;35:100959. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32244186 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase C Controls the Excitability of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons by Regulating Kv2.2 Channel Activity.Neurosci Bull. 2022 Feb;38(2):135-148. doi: 10.1007/s12264-021-00773-x. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Neurosci Bull. 2022. PMID: 34542799 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of Kv2.1-VAPA association provides neuroprotection against ischemic stroke in mice by declustering Kv2.1 channels.Sci Adv. 2020 Jul 1;6(27):eaaz8110. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz8110. Print 2020 Jul. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32937450 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Insights into Beta-cell Exocytosis in Type 2 Diabetes.J Mol Biol. 2020 Mar 6;432(5):1310-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.12.012. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31863749 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rorsman P, Braun M. Regulation of insulin secretion in human pancreatic islets. Annu Rev Physiol 2013;75:155–179 - PubMed
-
- MacDonald PE, Sewing S, Wang J, et al. . Inhibition of Kv2.1 voltage-dependent K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 2002;277:44938–44945 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

