Regulatory T Cells in Allergy and Asthma
- PMID: 28589115
- PMCID: PMC5440567
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2017.00117
Regulatory T Cells in Allergy and Asthma
Abstract
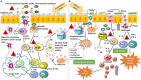
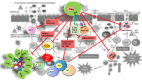
The immune system's correct functioning requires a sophisticated balance between responses to continuous microbial challenges and tolerance to harmless antigens, such as self-antigens, food antigens, commensal microbes, allergens, etc. When this equilibrium is altered, it can lead to inflammatory pathologies, tumor growth, autoimmune disorders, and allergy/asthma. The objective of this review is to show the existing data on the importance of regulatory T cells (Tregs) on this balance and to underline how intrauterine and postnatal environmental exposures influence the maturation of the immune system in humans. Genetic and environmental factors during embryo development and/or early life will result in a proper or, conversely, inadequate immune maturation with either beneficial or deleterious effects on health. We have focused herein on Tregs as a reflection of the maturity of the immune system. We explain the types, origins, and the mechanisms of action of these cells, discussing their role in allergy and asthma predisposition. Understanding the importance of Tregs in counteracting dysregulated immunity would provide approaches to diminish asthma and other related diseases in infants.
Keywords: FOXP3; allergy; asthma; children; immune system; inflammation; regulatory T cells; tolerance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thymic commitment of regulatory T cells is a pathway of TCR-dependent selection that isolates repertoires undergoing positive or negative selection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;293:43-71. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27702-1_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981475 Review.
-
Scientific rationale for the Finnish Allergy Programme 2008-2018: emphasis on prevention and endorsing tolerance.Allergy. 2009 May;64(5):678-701. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009.02024.x. Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19383025 Review.
-
Frequency and activation of CD4+CD25 FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in peripheral blood from children with atopic allergy.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;162(1):16-24. doi: 10.1159/000350769. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23817221
-
The regulation of allergy and asthma.Immunol Rev. 2006 Aug;212:238-55. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00413.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16903918 Review.
-
Low-grade disease activity in early life precedes childhood asthma and allergy.Dan Med J. 2016 Aug;63(8):B5272. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27477800 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in CD8+ regulatory T cell research.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jun;15(6):8187-8194. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8378. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29805553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin and Asthma: Knowns, Unknowns and Controversies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 20;22(16):8971. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168971. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How GRAIL controls Treg function to maintain self-tolerance.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1046631. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1046631. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569931 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiome and Metabolomics Profiles of Allergic and Non-Allergic Childhood Asthma.J Asthma Allergy. 2022 Apr 6;15:419-435. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S354870. eCollection 2022. J Asthma Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35418758 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Shrimp Tropomyosin-Mediated Allergy: Hypoallergen DNA Vaccines Induce Regulatory T Cells to Reduce Hypersensitivity in Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 19;20(18):4656. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184656. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31546958 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

