Myosin Va's adaptor protein melanophilin enforces track selection on the microtubule and actin networks in vitro
- PMID: 28559319
- PMCID: PMC5474823
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1619473114
Myosin Va's adaptor protein melanophilin enforces track selection on the microtubule and actin networks in vitro
Abstract
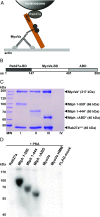
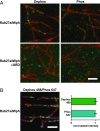
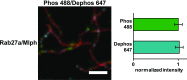
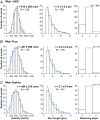
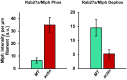
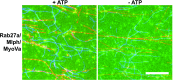
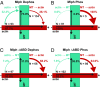
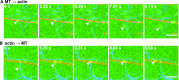
Pigment organelles, or melanosomes, are transported by kinesin, dynein, and myosin motors. As such, melanosome transport is an excellent model system to study the functional relationship between the microtubule- and actin-based transport systems. In mammalian melanocytes, it is well known that the Rab27a/melanophilin/myosin Va complex mediates actin-based transport in vivo. However, pathways that regulate the overall directionality of melanosomes on the actin/microtubule networks have not yet been delineated. Here, we investigated the role of PKA-dependent phosphorylation on the activity of the actin-based Rab27a/melanophilin/myosin Va transport complex in vitro. We found that melanophilin, specifically its C-terminal actin-binding domain (ABD), is a target of PKA. Notably, in vitro phosphorylation of the ABD closely recapitulated the previously described in vivo phosphorylation pattern. Unexpectedly, we found that phosphorylation of the ABD affected neither the interaction of the complex with actin nor its movement along actin tracks. Surprisingly, the phosphorylation state of melanophilin was instead important for reversible association with microtubules in vitro. Dephosphorylated melanophilin preferred binding to microtubules even in the presence of actin, whereas phosphorylated melanophilin associated with actin. Indeed, when actin and microtubules were present simultaneously, melanophilin's phosphorylation state enforced track selection of the Rab27a/melanophilin/myosin Va transport complex. Collectively, our results unmasked the regulatory dominance of the melanophilin adaptor protein over its associated motor and offer an unexpected mechanism by which filaments of the cytoskeletal network compete for the moving organelles to accomplish directional transport on the cytoskeleton in vivo.
Keywords: intracellular transport; melanophilin; myosin Va; transport regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The actin-binding domain of Slac2-a/melanophilin is required for melanosome distribution in melanocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(15):5245-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5245-5255.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12861011 Free PMC article.
-
More than just a cargo adapter, melanophilin prolongs and slows processive runs of myosin Va.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 11;288(41):29313-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476929. Epub 2013 Aug 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23979131 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptor protein melanophilin regulates dynamic myosin-Va:cargo interaction and dendrite development in melanocytes.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Mar 15;30(6):742-752. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-04-0237. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30699046 Free PMC article.
-
The melanosome as a model to study organelle motility in mammals.Pigment Cell Res. 2004 Apr;17(2):111-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0749.2004.00138.x. Pigment Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15016299 Review.
-
Myosin-V, a versatile motor for short-range vesicle transport.Traffic. 2002 Dec;3(12):859-65. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.31202.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 12453149 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory response: The target for treating hyperpigmentation during the repair of a burn wound.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1009137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1009137. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Permethrin Resistance on Aedes aegypti Transcriptome Following Ingestion of Zika Virus Infected Blood.Viruses. 2018 Sep 1;10(9):470. doi: 10.3390/v10090470. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 30200481 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo Roles of Rab27 and Its Effectors in Exocytosis.Cell Struct Funct. 2021 Nov 6;46(2):79-94. doi: 10.1247/csf.21043. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Cell Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 34483204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinesin-2 motors adapt their stepping behavior for processive transport on axonemes and microtubules.EMBO Rep. 2017 Nov;18(11):1947-1956. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744097. Epub 2017 Sep 8. EMBO Rep. 2017. PMID: 28887322 Free PMC article.
-
Roles and regulation of myosin V interaction with cargo.Adv Biol Regul. 2021 Jan;79:100787. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2021.100787. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Adv Biol Regul. 2021. PMID: 33541831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Vale RD. The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Cell. 2003;112:467–480. - PubMed
-
- Brown SS. Cooperation between microtubule- and actin-based motor proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:63–80. - PubMed
-
- Natarajan VT, Ganju P, Ramkumar A, Grover R, Gokhale RS. Multifaceted pathways protect human skin from UV radiation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:542–551. - PubMed
-
- Wei Q, Wu X, Hammer JA., 3rd The predominant defect in dilute melanocytes is in melanosome distribution and not cell shape, supporting a role for myosin V in melanosome transport. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1997;18:517–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

