Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 28555670
- PMCID: PMC5731833
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.49
Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
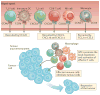
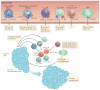
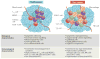
The tumour microenvironment is the primary location in which tumour cells and the host immune system interact. Different immune cell subsets are recruited into the tumour microenvironment via interactions between chemokines and chemokine receptors, and these populations have distinct effects on tumour progression and therapeutic outcomes. In this Review, we focus on the main chemokines that are found in the human tumour microenvironment; we elaborate on their patterns of expression, their regulation and their roles in immune cell recruitment and in cancer and stromal cell biology, and we consider how they affect cancer immunity and tumorigenesis. We also discuss the potential of targeting chemokine networks, in combination with other immunotherapies, for the treatment of cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCL7 Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1231:33-43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-36667-4_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32060844 Review.
-
The chemokine network: a target in cancer biology?Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006 Oct 1;58(8):962-74. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2006.03.012. Epub 2006 Aug 15. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006. PMID: 16996642 Review.
-
Chemokine-Directed Tumor Microenvironment Modulation in Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9804. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189804. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine systems in oncology: From microenvironment modulation to nanocarrier innovations.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 1):131679. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131679. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38641274 Review.
-
Improving homing in T cell therapy.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017 Aug;36:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.06.009. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017. PMID: 28690108 Review.
Cited by
-
SHP2 inhibition diminishes KRASG12C cycling and promotes tumor microenvironment remodeling.J Exp Med. 2021 Jan 4;218(1):e20201414. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201414. J Exp Med. 2021. PMID: 33045063 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring cell-derived extracellular vesicles in peripheral blood and bone marrow of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia pediatric patients: proof-of-concept study.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1421036. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421036. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39234258 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 3 as a Recurrence Risk Factor and a Potential Molecular Therapeutic Target in Colorectal Cancer.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 2;13:427-438. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S252157. eCollection 2020. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33061521 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic cell death mediation patterns reveal novel paradigm for characterizing the immune microenvironment and immunotherapeutic responses in bladder cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 25;13:1035484. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1035484. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36386817 Free PMC article.
-
High-dimensional single-cell proteomics analysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals dynamic alterations of the tumor immune microenvironment after neoadjuvant therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):e007847. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007847. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38016720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rot A, von Andrian UH. Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: basic chemokinese grammar for immune cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:891–928. - PubMed
-
- Griffith JW, Sokol CL, Luster AD. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2014;32:659–702. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. This is a comprehensive review of chemokines and chemokine receptors and their roles in tumour development. - PubMed
-
- Zou W. Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:263–274. This thorough review highlights tumour and immune interactions that create an immunosuppressive and tolerizing microenvironment, and describes how their manipulation can influence therapeutic outcomes. - PubMed
-
- Zou W. Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:295–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA092562/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA193136/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA189440/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA171306/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA217510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA152470/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA156685/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA190176/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA211016/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA123088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA100227/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA099985/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

