Aerobic exercise combined with huwentoxin-I mitigates chronic cerebral ischemia injury
- PMID: 28553340
- PMCID: PMC5436358
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.205099
Aerobic exercise combined with huwentoxin-I mitigates chronic cerebral ischemia injury
Abstract
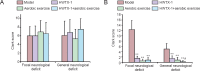
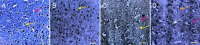
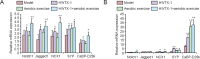
Ca2+ channel blockers have been shown to protect neurons from ischemia, and aerobic exercise has significant protective effects on a variety of chronic diseases. The present study injected huwentoxin-I (HWTX-I), a spider peptide toxin that blocks Ca2+ channels, into the caudal vein of a chronic cerebral ischemia mouse model, once every 2 days, for a total of 15 injections. During this time, a subgroup of mice was subjected to treadmill exercise for 5 weeks. Results showed amelioration of cortical injury and improved neurological function in mice with chronic cerebral ischemia in the HWTX-I + aerobic exercise group. The combined effects of HWTX-I and exercise were superior to HWTX-I or aerobic exercise alone. HWTX-I effectively activated the Notch signal transduction pathway in brain tissue. Aerobic exercise up-regulated synaptophysin mRNA expression. These results demonstrated that aerobic exercise, in combination with HWTX-I, effectively relieved neuronal injury induced by chronic cerebral ischemia via the Notch signaling pathway and promoting synaptic regeneration.
Keywords: Notch signaling pathway; aerobic exercise; calcium overload; chronic cerebral ischemia; huwentoxin-I; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Aerobic exercise combined with huwentoxin-I upregulates phase-Ⅱ detoxification enzymes to alleviate obstructive jaundice-induced central nervous system injury in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Aug 30;40(8):1192-1199. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.08.18. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32895170 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effect of Huwentoxin-I on the Fas and TNF apoptosis pathway in the hippocampus of rat with global cerebral ischemia.Toxicon. 2007 Dec 15;50(8):1085-94. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2007.07.020. Epub 2007 Aug 7. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17900647
-
Direct evidence for high affinity blockade of NaV1.6 channel subtype by huwentoxin-IV spider peptide, using multiscale functional approaches.Neuropharmacology. 2018 May 1;133:404-414. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29474819
-
Huwentoxin-XVI, an analgesic, highly reversible mammalian N-type calcium channel antagonist from Chinese tarantula Ornithoctonus huwena.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:657-67. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.017. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24467846
-
Synthesis and biological characterization of synthetic analogs of Huwentoxin-IV (Mu-theraphotoxin-Hh2a), a neuronal tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channel inhibitor.Toxicon. 2013 Sep;71:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 May 29. Toxicon. 2013. PMID: 23726857
Cited by
-
Treadmill training improves neurological deficits and suppresses neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke rats.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Aug;14(8):1387-1393. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.253523. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30964064 Free PMC article.
-
[Aerobic exercise combined with huwentoxin-I upregulates phase-Ⅱ detoxification enzymes to alleviate obstructive jaundice-induced central nervous system injury in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Aug 30;40(8):1192-1199. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.08.18. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32895170 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Aerobic Exercise Inhibits CUMS-Depressed Mice Hippocampal Inflammatory Response via Activating Hippocampal miR-223/TLR4/MyD88-NF-κB Pathway.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 14;17(8):2676. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082676. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32295141 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of seven exercise interventions for symptoms of depression in college students: A network of meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 20;99(47):e23058. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023058. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33217806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antipenko EA, Deryugina AV, Gustov AV. The system stress-limiting action of mexidol in chronic cerebral ischemia. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2016;116:28–31. - PubMed
-
- Arteaga O, Revuelta M, Urigüen L, Martínez-Millán L, Hilario E, Álvarez A. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces cerebral damage and ameliorates long-term cognitive impairments caused by neonatal hypoxia–ischemia in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 2016 doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0221-8:1-19. - PubMed
-
- Boscia F, Casamassa A, Secondo A, Esposito A, Pannaccione A, Sirabella R, Pignataro G, Cuomo O, Vinciguerra A, de Rosa V, Annunziato L. NCX1 exchanger cooperates with calretinin to confer preconditioning-induced tolerance against cerebral ischemia in the striatum. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53:1365–1376. - PubMed
-
- Cechetti F, Worm PV, Elsner VR, Bertoldi K, Sanches E, Ben J, Siqueira IR, Netto CA. Forced treadmill exercise prevents oxidative stress and memory deficits following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012;97:90–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

