Divergent Expression of CXCR5 and CCR5 on CD4+ T Cells and the Paradoxical Accumulation of T Follicular Helper Cells during HIV Infection
- PMID: 28553284
- PMCID: PMC5427074
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00495
Divergent Expression of CXCR5 and CCR5 on CD4+ T Cells and the Paradoxical Accumulation of T Follicular Helper Cells during HIV Infection
Abstract
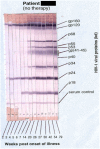
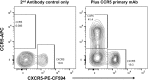
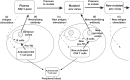
Viral infection sets in motion a cascade of immune responses, including both CXCR5+CD4+ T follicular helper (Tfh) cells that regulate humoral immunity and CCR5+CD4+ T cells that mediate cell-mediated immunity. In peripheral blood mononuclear cells, the majority of memory CD4+ T cells appear to fall into either of these two lineages, CCR5-CXCR5+ or CCR5+CXCR5-. Very high titers of anti-HIV IgG antibodies are a hallmark of infection, strongly suggesting that there is significant HIV-specific CD4+ T cell help to HIV-specific B cells. We now know that characteristic increases in germinal centers (GC) in lymphoid tissue (LT) during SIV and HIV-1 infections are associated with an increase in CXCR5+PD-1high Tfh, which expand to a large proportion of memory CD4+ T cells in LT, and are presumably specific for SIV or HIV epitopes. Macaque Tfh normally express very little CCR5, yet are infected by CCR5-using SIV, which may occur mainly through infection of a subset of PD-1intermediateCCR5+Bcl-6+ pre-Tfh cells. In contrast, in human LT, a subset of PD-1high Tfh appears to express low levels of CCR5, as measured by flow cytometry, and this may also contribute to the high rate of infection of Tfh. Also, we have found, by assessing fine-needle biopsies of LT, that increases in Tfh and GC B cells in HIV infection are not completely normalized by antiretroviral therapy (ART), suggesting a possible long-lasting reservoir of infected Tfh. In contrast to the increase of CXCR5+ Tfh, there is no accumulation of proliferating CCR5+ CD4 T HIV Gag-specific cells in peripheral blood that make IFN-γ. Altogether, CXCR5+CCR5- CD4 T cells that regulate humoral immunity are allowed greater freedom to operate and expand during HIV-1 infection, but at the same time can contain HIV DNA at levels at least as high as in other CD4 subsets. We argue that early ART including a CCR5 blocker may directly reduce the infected Tfh reservoir in LT and also interrupt cycles of antibody pressure driving virus mutation and additional GC responses to resulting neoantigens.
Keywords: CD4+ T lymphocytes; HIV; T follicular helper cells; germinal centers; lymphoid tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 and SIV Predominantly Use CCR5 Expressed on a Precursor Population to Establish Infection in T Follicular Helper Cells.Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 21;8:376. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00376. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28484447 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Drives Differentiation, Aberrant Accumulation, and Latent Infection of Germinal Center Follicular T Helper Cells.J Virol. 2015 Nov 25;90(3):1578-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02471-15. Print 2016 Feb 1. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26608323 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of circulating T follicular helper cells is associated with disease progression in HIV-infected individuals.J Infect Public Health. 2018 Sep-Oct;11(5):685-690. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Mar 1. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29409739
-
Tfh1 Cells in Germinal Centers During Chronic HIV/SIV Infection.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 6;9:1272. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01272. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29928280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4 T Follicular Helper and Regulatory Cell Dynamics and Function in HIV Infection.Front Immunol. 2016 Dec 27;7:659. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00659. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 28082992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Follicular Dendritic Cells of Lymph Nodes as Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Reservoirs and Insights on Cervical Lymph Node.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 19;9:805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00805. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29725333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normal human lymph node T follicular helper cells and germinal center B cells accessed via fine needle aspirations.J Immunol Methods. 2020 Apr;479:112746. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2020.112746. Epub 2020 Jan 17. J Immunol Methods. 2020. PMID: 31958451 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal CD4 Depletion in HIV / SIV Infection.Curr Immunol Rev. 2019;15(1):76-91. doi: 10.2174/1573395514666180605083448. Curr Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31431807 Free PMC article.
-
Early expansion of CD38+ICOS+ GC Tfh in draining lymph nodes during influenza vaccination immune response.iScience. 2021 Dec 18;25(1):103656. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103656. eCollection 2022 Jan 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 35028536 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Infectious Agent-Induced Chronic Immune Activation: Causes, Phenotypes, and Consequences.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 10;12:740556. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.740556. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956176 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Levy JA. HIV and the Pathogenesis of AIDS. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; (1998).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

