RpoN Promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa Survival in the Presence of Tobramycin
- PMID: 28553272
- PMCID: PMC5427110
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00839
RpoN Promotes Pseudomonas aeruginosa Survival in the Presence of Tobramycin
Abstract
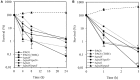
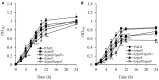
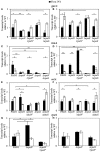
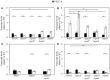
Pseudomonas aeruginosa has developed diverse strategies to respond and adapt to antibiotic stress. Among the factors that modulate survival in the presence of antibiotics, alternative sigma factors play an important role. Here, we demonstrate that the alternative sigma factor RpoN (σ54) promotes survival in the presence of tobramycin. The tobramycin-sensitive phenotype of logarithmic phase ΔrpoN mutant cells is suppressed by the loss of the alternative sigma factor RpoS. Transcriptional analysis indicated that RpoN positively regulates the expression of RsmA, an RNA-binding protein, in the P. aeruginosa stationary growth phase in a nutrient-rich medium. The loss of RpoS led to the upregulation of gacA expression in the nutrient-limited medium-grown stationary phase cells. Conversely, in the logarithmic growth phase, the ΔrpoS mutant demonstrated lower expression of gacA, underscoring a regulatory role of RpoS for GacA. Supplementation of tobramycin to stationary phase ΔrpoN mutant cells grown in nutrient-rich medium resulted in decreased expression of gacA, relA, and rpoS without altering the expression of rsmA relative to wild-type PAO1. The observed downregulation of gacA and relA in the ΔrpoN mutant in the presence of tobramycin could be reversed through the mutation of rpoS in the ΔrpoN mutant background. The tobramycin-tolerant phenotype of the ΔrpoNΔrpoS mutant logarithmic phase cells may be associated with the expression of relA, which remained unresponsive upon addition of tobramycin. The logarithmic phase ΔrpoS and ΔrpoNΔrpoS mutant cells demonstrated increased expression of gacA in response to tobramycin. Together, these results suggest that a complex regulatory interaction between RpoN, RpoS, the Gac/Rsm pathway, and RelA modulates the P. aeruginosa response to tobramycin.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; RpoN; RpoS; antibiotic tolerance; tobramycin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RpoN Modulates Carbapenem Tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal and PqsE.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Sep 23;60(10):5752-64. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00260-16. Print 2016 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27431228 Free PMC article.
-
Potentiation of Aminoglycoside Lethality by C4-Dicarboxylates Requires RpoN in Antibiotic-Tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e01313-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01313-19. Print 2019 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31383655 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of co-deficiency of RpoN and RpoS on stress tolerance, virulence and gene regulation in Edwardsiella tarda.J Basic Microbiol. 2014 Jul;54(7):678-87. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201300622. Epub 2014 Mar 14. J Basic Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24633758
-
Regulatory function of sigma factors RpoS/RpoN in adaptation and spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica.Food Microbiol. 2021 Aug;97:103755. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2021.103755. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Food Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33653528
-
Control of rpoS transcription in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas: why so different?Mol Microbiol. 2003 Jul;49(1):1-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03547.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12823806 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term evolution of antibiotic tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections.Evol Lett. 2023 Sep 20;7(6):389-400. doi: 10.1093/evlett/qrad034. eCollection 2023 Dec. Evol Lett. 2023. PMID: 38045720 Free PMC article.
-
Response regulator VemR regulates the transcription of flagellar rod gene flgG by interacting with σ54 factor RpoN2 in Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri.Mol Plant Pathol. 2019 Mar;20(3):372-381. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12762. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Mol Plant Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30353625 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteamine Inhibits Glycine Utilisation and Disrupts Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Sep 22;11:718213. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.718213. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34631600 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking RpoN reduces virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis patients and increases antibiotic sensitivity in a laboratory strain.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 30;9(1):6677. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43060-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31040330 Free PMC article.
-
The RavA/VemR two-component system plays vital regulatory roles in the motility and virulence of Xanthomonas campestris.Mol Plant Pathol. 2022 Mar;23(3):355-369. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13164. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Mol Plant Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34837306 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

