Docking Studies and Biological Evaluation of a Potential β-Secretase Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxyhericenone F from Hericium erinaceus
- PMID: 28553224
- PMCID: PMC5427148
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00219
Docking Studies and Biological Evaluation of a Potential β-Secretase Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxyhericenone F from Hericium erinaceus
Abstract
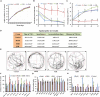
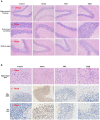
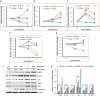
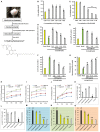
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder, affecting approximately more than 5% of the population worldwide over the age 65, annually. The incidence of AD is expected to be higher in the next 10 years. AD patients experience poor prognosis and as a consequence new drugs and therapeutic strategies are required in order to improve the clinical responses and outcomes of AD. The purpose of the present study was to screen a certain number of potential compounds from herbal sources and investigate their corresponding mode of action. In the present study, the learning and memory effects of ethanol:water (8:2) extracts from Hericium erinaceus were evaluated on a dementia rat model. The model was established by intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg/d D-galactose in rats. The results indicated that the extracts can significantly ameliorate the learning and memory abilities. Specific active ingredients were screened in vivo assays and the results were combined with molecular docking studies. Potential receptor-ligand interactions on the BACE1-inhibitor namely, 3-Hydroxyhericenone F (3HF) were investigated. The isolation of a limited amount of 3HF from the fruit body of H. erinaceus by chemical separation was conducted, and the mode of action of this compound was verified in NaN3-induced PC12 cells. The cell-based assays demonstrated that 3HF can significantly down-regulate the expression of BACE1 (p < 0.01), while additional AD intracellular markers namely, p-Tau and Aβ1-42 were further down-regulated (p < 0.05). The data further indicate that 3HF can ameliorate certain mitochondrial dysfunction conditions by the reversal of the decreasing level of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes, the calcium ion levels ([Ca2+]), the inhibiton in the production of ROS, the increase in the mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP levels, and the regulation of the expression levels of the genes encoding for the p21, COX I, COX II, PARP1, and NF-κB proteins. The observations suggest the use of H. erinaceus in traditional medicine for the treatment of various neurological diseases and render 3HF as a promising naturally occurring chemical constituent for the treatment of AD via the inhibition of the β-secretase enzyme.
Keywords: 3-Hydroxyhericenone F; Alzheimer’s disease; Hericium erinaceus; active pharmaceutical ingredient; functional foods; molecular docking; regulatory mechanism.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Monkey Head Mushroom and Memory Enhancement in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2022 Jul 24;11(15):2284. doi: 10.3390/cells11152284. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35892581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Mechanisms and Potential Implications of Hericium erinaceus in NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Reactive Oxygen Species during Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 22;10(11):1664. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111664. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829535 Free PMC article.
-
Hericium erinaceus (Bull.) Pers. Ethanolic Extract with Antioxidant Properties on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits in a Zebrafish Model of Cognitive Impairment.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jun 12;7(6):477. doi: 10.3390/jof7060477. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204787 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor-inducing activity of Hericium erinaceus in 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells.Biol Pharm Bull. 2008 Sep;31(9):1727-32. doi: 10.1248/bpb.31.1727. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008. PMID: 18758067
-
Therapeutic potentials of plant iridoids in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases: A review.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 May 1;169:185-199. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30877973 Review.
Cited by
-
Lion's Mane (Hericium erinaceus) Exerts Anxiolytic Effects in the rTg4510 Tau Mouse Model.Behav Sci (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;12(7):235. doi: 10.3390/bs12070235. Behav Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35877305 Free PMC article.
-
Prebiotic Effect of Fructooligosaccharides from Morinda officinalis on Alzheimer's Disease in Rodent Models by Targeting the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Dec 8;9:403. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00403. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29276488 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the possible mechanisms in kouyanqing granule for treatment of oral ulcers based on network pharmacology.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Aug 18;20(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03043-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32811507 Free PMC article.
-
Hypouricemic Effects of Ganoderma applanatum in Hyperuricemia Mice through OAT1 and GLUT9.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 15;8:996. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00996. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29379442 Free PMC article.
-
Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer's Disease Control.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 22;15(23):4878. doi: 10.3390/nu15234878. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandalise F., Cesaroni V., Gregori A., Repetti M., Romano C., Orrù G., et al. (2017). Dietary supplementation of Hericium erinaceus increases mossy fiber-CA3 hippocampal neurotransmission and recognition memory in wild-type mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017:3864340 10.1155/2017/3864340 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

