Characterization of Juvenile Hormone Related Genes Regulating Cantharidin Biosynthesis in Epicauta chinensis
- PMID: 28536442
- PMCID: PMC5442126
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02393-w
Characterization of Juvenile Hormone Related Genes Regulating Cantharidin Biosynthesis in Epicauta chinensis
Abstract
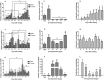
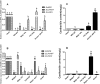
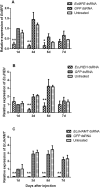
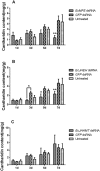
Cantharidin is a defensive toxin biosynthesized by blister beetles. It is well known for medical applications and toxicity. However, the biosynthesis process of cantharidin is still not well understood. In the present study, three genes (methyl farnesoate epoxidase (EcMFE), juvenile hormone acid O-methyltransferase (EcJHAMT) and juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (EcJHEH)) were identified from Epicauta chinensis. The temporal and spatial expression patterns of these three genes revealed that the expression levels of EcMFE and EcJHEH were high in the first instar larval stage of E. chinensis with EcJHEH transcripts highest in the fifth larval instar. The expression level of EcJHAMT was significantly higher in the 2nd and 3rd larval instars. The transcripts of EcMFE, EcJHEH and EcJHAMT showed a similar tendency with the cantharidin production in male blister beetles after mating. We verified the functions of these three genes in cantharidin biosynthesis using the RNA interference method. Interference of EcMFE and EcJHEH significantly inhibited the biosynthesis of cantharidin in male E. chinensis after mating, but interference of EcJHAMT has no apparent influence on cantharidin biosynthesis. We propose that EcMFE and EcJHEH may be involved in the biosynthesis of cantharidin, but JH III might not be the direct precursor of cantharidin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterized cantharidin distribution and related gene expression patterns in tissues of blister beetles, Epicauta chinensis.Insect Sci. 2019 Apr;26(2):240-250. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12512. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Insect Sci. 2019. PMID: 28745022
-
3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase: an essential actor in the biosynthesis of cantharidin in the blister beetle Epicauta chinensis Laporte.Insect Mol Biol. 2016 Feb;25(1):58-71. doi: 10.1111/imb.12198. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Insect Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26566751
-
The Potential Organ Involved in Cantharidin Biosynthesis in Epicauta chinensis Laporte (Coleoptera: Meloidae).J Insect Sci. 2017 Jan 1;17(2):52. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iex021. J Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 28423415 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry of proteins that bind and metabolize juvenile hormones.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996;32(3-4):407-19. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1996)32:3/4<407::AID-ARCH13>3.0.CO;2-G. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8756303 Review.
-
Cantharidin.Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2024 Apr;40(1):113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.cveq.2023.08.002. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 2024. PMID: 37716858 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Occurring Terpene Cyclic Anhydrides: Biosynthetic Origin and Biological Activities.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 6;14(8):955. doi: 10.3390/biom14080955. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Discovery Insights from Medicinal Beetles in Traditional Chinese Medicine.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2021 Mar 1;29(2):105-126. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.229. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 33632986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Draft Genome of a Blister Beetle Mylabris aulica.Front Genet. 2020 Jan 8;10:1281. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01281. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32010178 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the role of male reproductive tract and haemolymph in cantharidin-exuding Lydus trimaculatus and Mylabris variabilis (Coleoptera: Meloidae): a comparative transcriptomics approach.BMC Genomics. 2021 Nov 8;22(1):808. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08118-8. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34749651 Free PMC article.
-
Functional studies of McSTE24, McCYP305a1, and McJHEH, three essential genes act in cantharidin biosynthesis in the blister beetle (Coleoptera: Meloidae).J Insect Sci. 2024 Jul 1;24(4):4. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieae070. J Insect Sci. 2024. PMID: 38989843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dettner, K. in Inter-and intraspecific transfer of toxic insect compound cantharidin. Vertical food web interactions 115–145 (Springer, 1997).
-
- Nikbakhtzadeh MR, Hemp C, Ebrahimi B. Further evidence for the role of cantharidin in the mating behaviour of blister beetles (Coleoptera: Meloidae) Integrative biosciences. 2007;11:141–146. doi: 10.1080/17386357.2007.9647327. - DOI
-
- Nikbakhtzadeh MR, Dettner K, Boland W, Hemp C. The possible role of antennal cuticular pores in the sexual behaviour of Cyaneolytta sp.(Coleoptera: Meloidae) Mitt Dtsch Ges Allg Angew Ent. 2008;16:179–183.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

