Theranostic Performance of Acoustic Nanodroplet Vaporization-Generated Bubbles in Tumor Intertissue
- PMID: 28529631
- PMCID: PMC5436507
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.19099
Theranostic Performance of Acoustic Nanodroplet Vaporization-Generated Bubbles in Tumor Intertissue
Abstract
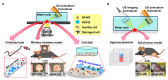
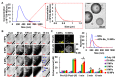
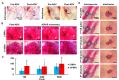
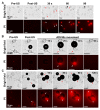
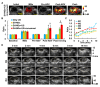
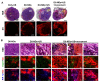
Solid tumors with poorly perfused regions reveal some of the treatment limitations that restrict drug delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Acoustic droplet vaporization (ADV) has been applied to directly disrupt vessels and release nanodroplets, ADV-generated bubbles (ADV-Bs), and drugs into tumor tissue. In this study, we investigated the in vivo behavior of ADV-Bs stimulated by US, and evaluated the possibility of moving intertissue ADV-Bs into the poorly perfused regions of solid tumors. Intravital imaging revealed intertissue ADV-B formation, movement, and cavitation triggered by US, where the distance of intertissue ADV-B movement was 33-99 µm per pulse. When ADV-Bs were applied to tumor cells, the cell membrane was damaged, increasing cellular permeability or inducing cell death. The poorly perfused regions within solid tumors show enhancement due to ADV-B accumulation after application of US-triggered ADV-B. The intratumoral nanodroplet or ADV-B distribution around the poorly perfused regions with tumor necrosis or hypoxia were demonstrated by histological assessment. ADV-B formation, movement and cavitation could induce cell membrane damage by mechanical force providing a mechanism to overcome treatment limitations in poorly perfused regions of tumors.
Keywords: acoustic droplet vaporization; bubble cavitation.; intertissue bubbles; nanodroplets; poorly perfused regions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concurrent anti-vascular therapy and chemotherapy in solid tumors using drug-loaded acoustic nanodroplet vaporization.Acta Biomater. 2017 Feb;49:472-485. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.11.018. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27836803
-
Camptothecin-loaded fusogenic nanodroplets as ultrasound theranostic agent in stem cell-mediated drug-delivery system.J Control Release. 2018 May 28;278:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 6. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29630986
-
In situ observation of single cell response to acoustic droplet vaporization: Membrane deformation, permeabilization, and blebbing.Ultrason Sonochem. 2018 Oct;47:141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018. PMID: 29678490
-
Acoustic droplet vaporization in biology and medicine.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:404361. doi: 10.1155/2013/404361. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24350267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Micro- to Nano-Multifunctional Theranostic Platform: Effective Ultrasound Imaging Is Not Just a Matter of Scale.Mol Imaging. 2018 Jan-Dec;17:1536012118778216. doi: 10.1177/1536012118778216. Mol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30213222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondria-Targeted Nanocarriers Promote Highly Efficient Cancer Therapy: A Review.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 12;9:784602. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.784602. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34869294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective intracellular delivery of perfluorocarbon nanodroplets for cytotoxicity threshold reduction on ultrasound-induced vaporization.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2019 Aug;2(4):e1165. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1165. Epub 2019 Feb 17. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 32721118 Free PMC article.
-
A Study on the Acoustic Response of Pickering Perfluoropentane Droplets in Different Media.ACS Omega. 2021 Feb 17;6(8):5670-5678. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c06115. eCollection 2021 Mar 2. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 33681606 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-transition nanodroplets with immunomodulatory capabilities for potentiating mild magnetic hyperthermia to inhibit tumour proliferation and metastasis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Apr 17;21(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01885-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37069614 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the Compressibility of Cellulose Nanofiber-Stabilized Microdroplets Using Acoustophoresis.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Nov 27;12(12):1465. doi: 10.3390/mi12121465. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34945315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in psoriasis: therapeutic implications. J Invest Dermatol. 1972;59:40–3. - PubMed
-
- Vaupel P. The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression. Oncologist. 2004;9(Suppl 5):10–7. - PubMed
-
- Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:136–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

