SGLT2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Option for Diabetic Nephropathy
- PMID: 28524098
- PMCID: PMC5454992
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18051083
SGLT2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Option for Diabetic Nephropathy
Abstract
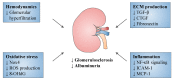
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) worldwide. Glycemic and blood pressure (BP) control are important but not sufficient to attenuate the incidence and progression of DN. Sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors are a new class of glucose-lowering agent suggested to exert renoprotective effects in glucose lowering-dependent and independent fashions. Experimental studies have shown that SGLT2 inhibitors attenuate DN in animal models of both type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D), indicating a potential renoprotective effect beyond glucose reduction. Renoprotection by SGLT2 inhibitors has been demonstrated in T2D patients with a high cardiovascular risk in randomized controlled trials (RCTs). These favorable effects of SGLT2 inhibitors are explained by several potential mechanisms, including the attenuation of glomerular hyperfiltration, inflammation and oxidative stress. In this review article, we discuss the renoprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibitors by integrating experimental findings with the available clinical data.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; cardiovascular disease; diabetic nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in association with this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Diabetic Kidney.Diabetes Care. 2016 Aug;39 Suppl 2:S165-71. doi: 10.2337/dcS15-3006. Diabetes Care. 2016. PMID: 27440829
-
The roles of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in preventing kidney injury in diabetes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Oct;94:176-187. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.095. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28759755 Review.
-
Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and prevention of diabetic nephropathy: targeting the renal tubule in diabetes.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jul;64(1):16-24. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24673844 Review.
-
SGLT-2 inhibitors in Diabetic Kidney Disease: What Lies Behind their Renoprotective Properties?Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(29):5564-5578. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180524114033. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29792136
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 1 diabetes: simultaneous glucose lowering and renal protection?Can J Diabetes. 2014 Oct;38(5):356-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Can J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 25192954 Review.
Cited by
-
Breaking boundaries in diabetic nephropathy treatment: design and synthesis of novel steroidal SGLT2 inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Oct 15. doi: 10.1039/d4md00645c. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39479473 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Empagliflozin on the Outcomes of β-Thalassemia Major in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The THALEMPA Observational Study.Cureus. 2024 Sep 21;16(9):e69837. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69837. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39435207 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a marker for renal outcome of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) (U-CARE study 3).BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024 May 30;12(3):e004237. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2024-004237. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2024. PMID: 38816205 Free PMC article.
-
Dapagliflozin mitigates oxidative stress, inflammatory, and histopathological markers of aging in mice.J Med Life. 2024 Feb;17(2):157-163. doi: 10.25122/jml-2023-0343. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 38813367 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and Renal Complications: An Overview on Pathophysiology, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Interventions.Biomedicines. 2024 May 15;12(5):1098. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12051098. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38791060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stratton I.M., Adler A.I., Neil H.A., Matthews D.R., Manley S.E., Cull C.A., Hadden D., Turner R.C., Holman R.R. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): Prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:405–412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7258.405. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

