Anti-Inflammatory Effects of OxPAPC Involve Endothelial Cell-Mediated Generation of LXA4
- PMID: 28522438
- PMCID: PMC5886749
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310308
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of OxPAPC Involve Endothelial Cell-Mediated Generation of LXA4
Abstract
Rationale: Oxidation of 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine (OxPAPC) generates a group of bioactive oxidized phospholipid products with a broad range of biological activities. Barrier-enhancing and anti-inflammatory effects of OxPAPC on pulmonary endothelial cells are critical for prevention of acute lung injury caused by bacterial pathogens or excessive mechanical ventilation. Anti-inflammatory properties of OxPAPC are associated with its antagonistic effects on Toll-like receptors and suppression of RhoA GTPase signaling.
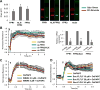
Objective: Because OxPAPC exhibits long-lasting anti-inflammatory and lung-protective effects even after single administration in vivo, we tested the hypothesis that these effects may be mediated by additional mechanisms, such as OxPAPC-dependent production of anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediator, lipoxin A4 (LXA4).
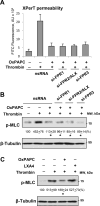
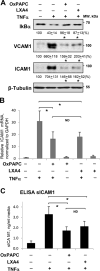
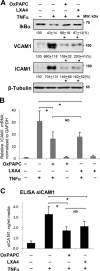
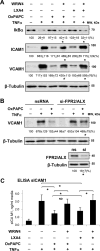
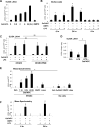
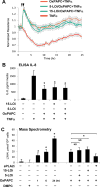
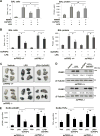
Methods and results: Mass spectrometry and ELISA assays detected significant accumulation of LXA4 in the lungs of OxPAPC-treated mice and in conditioned medium of OxPAPC-exposed pulmonary endothelial cells. Administration of LXA4 reproduced anti-inflammatory effect of OxPAPC against tumor necrosis factor-α in vitro and in the animal model of lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. The potent barrier-protective and anti-inflammatory effects of OxPAPC against tumor necrosis factor-α and lipopolysaccharide challenge were suppressed in human pulmonary endothelial cells with small interfering RNA-induced knockdown of LXA4 formyl peptide receptor-2 (FPR2/ALX) and in mFPR2-/- (mouse formyl peptide receptor 2) mice lacking the mouse homolog of human FPR2/ALX.
Conclusions: This is the first demonstration that inflammation- and injury-associated phospholipid oxidation triggers production of anti-inflammatory and proresolution molecules, such as LXA4. This lipid mediator switch represents a novel mechanism of OxPAPC-assisted recovery of inflamed lung endothelium.
Keywords: endothelial cells; inflammation; lipoxins; lung injury; phospholipids; pulmonary circulation.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Control of Endothelial Barrier Function: Mechanisms and Implication in Lung Injury.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 23;12:794437. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.794437. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34887839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E receptor-4 receptor mediates endothelial barrier-enhancing and anti-inflammatory effects of oxidized phospholipids.FASEB J. 2017 Sep;31(9):4187-4202. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601232RR. Epub 2017 Jun 1. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28572443 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized phospholipids protect against lung injury and endothelial barrier dysfunction caused by heat-inactivated Staphylococcus aureus.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):L550-62. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00248.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25575515 Free PMC article.
-
Akt-mediated transactivation of the S1P1 receptor in caveolin-enriched microdomains regulates endothelial barrier enhancement by oxidized phospholipids.Circ Res. 2009 Apr 24;104(8):978-86. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.193367. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19286607 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Healthy and Diseased Lung Endothelium.Cells. 2020 Apr 15;9(4):981. doi: 10.3390/cells9040981. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidized Phospholipids in Control of Endothelial Barrier Function: Mechanisms and Implication in Lung Injury.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 23;12:794437. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.794437. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34887839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NRF2 regulates endothelial glycolysis and proliferation with miR-93 and mediates the effects of oxidized phospholipids on endothelial activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 16;46(3):1124-1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1155. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29161413 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxins in the Nervous System: Brighter Prospects for Neuroprotection.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 26;13:781889. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.781889. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35153778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Interference Attenuates Inflammation In Bacillus Endophthalmitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Nov 2;61(13):17. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.13.17. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33180117 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental Role of miRNA-144-3p in Intracerebral Hemorrhage Induced Secondary Brain Injury is Mediated by Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 Downregulation Both In Vivo and In Vitro.Cell Transplant. 2019 Jun;28(6):723-738. doi: 10.1177/0963689718817219. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30511586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subbanagounder G, Wong JW, Lee H, Faull KF, Miller E, Witztum JL, Berliner JA. Epoxyisoprostane and epoxycyclopentenone phospholipids regulate monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and interleukin-8 synthesis. Formation of these oxidized phospholipids in response to interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(9):7271–7281. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Malyukova I, Mikaelyan A, Fu P, Birukov KG. Tiam1 and betaPIX mediate Rac-dependent endothelial barrier protective response to oxidized phospholipids. J Cell Physiol. 2007;211(3):608–617. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

