Hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 28493839
- PMCID: PMC5542303
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17358
Hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
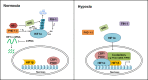
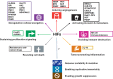
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most prevalent and lethal cancers with limited therapeutic options. Pathogenesis of this disease involves tumor hypoxia and the activation of hypoxia inducible factors. In this review, we describe the current understanding of hypoxia signaling pathway and summarize the expression, function and target genes of hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. We also highlight the recent progress in hypoxia-targeted therapeutic strategies in hepatocellular carcinoma and discuss further the future efforts for the study of hypoxia and/or hypoxia inducible factors in this deadly disease.
Keywords: HIF; hepatoma; hypoxia; liver cancer; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stable knockdown of CREB, HIF-1 and HIF-2 by replication-competent retroviruses abrogates the responses to hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2017 Feb;24(2):64-74. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2016.68. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 27934882 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1α promoted vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma through LOXL2 up-regulation in hypoxic tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 27;36(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0533-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28449718 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:409272. doi: 10.1155/2014/409272. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25101278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12171-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ever-expanding role of HIF in tumour and stromal biology.Nat Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;18(4):356-65. doi: 10.1038/ncb3330. Nat Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27027486 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Profiling of Porcine HCC Xenografts Provides Insights Into Tumor Cell Microenvironment Signaling.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 29;12:657330. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.657330. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33995488 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Bases of Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 23;12(6):1663. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061663. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32585893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Kaempferol Loaded Nanoparticles against Experimentally Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 5;13(12):2086. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122086. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959368 Free PMC article.
-
Phenylethanol glycosides from Herba Cistanche improve the hypoxic tumor microenvironment and enhance the effects of oxaliplatin via the HIF‑1α signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):517. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12156. Epub 2021 May 20. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34013363 Free PMC article.
-
Yes-associated protein (YAP) binds to HIF-1α and sustains HIF-1α protein stability to promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell glycolysis under hypoxic stress.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 4;37(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0892-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30180863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Global Cancer Facts & Figures. 3. 2015.
-
- Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S35–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

